Cancer-associated TERT promoter mutations abrogate telomerase silencing
- PMID: 26194807
- PMCID: PMC4507476
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.07918
Cancer-associated TERT promoter mutations abrogate telomerase silencing
Abstract
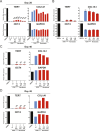
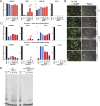
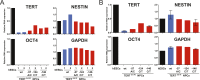
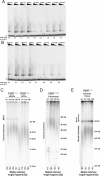
Mutations in the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter are the most frequent non-coding mutations in cancer, but their molecular mechanism in tumorigenesis has not been established. We used genome editing of human pluripotent stem cells with physiological telomerase expression to elucidate the mechanism by which these mutations contribute to human disease. Surprisingly, telomerase-expressing embryonic stem cells engineered to carry any of the three most frequent TERT promoter mutations showed only a modest increase in TERT transcription with no impact on telomerase activity. However, upon differentiation into somatic cells, which normally silence telomerase, cells with TERT promoter mutations failed to silence TERT expression, resulting in increased telomerase activity and aberrantly long telomeres. Thus, TERT promoter mutations are sufficient to overcome the proliferative barrier imposed by telomere shortening without additional tumor-selected mutations. These data establish that TERT promoter mutations can promote immortalization and tumorigenesis of incipient cancer cells.
Keywords: CRISPR/CRISPR-associated systems 9 CAS9; cancer mechanism; chromosomes; developmental biology; genes; genome editing; human; immortalization; stem cells; telomerase TERT; tumor spectrum.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
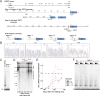
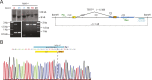
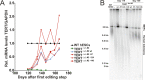
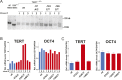
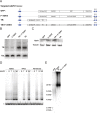
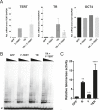
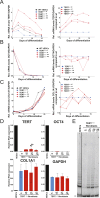
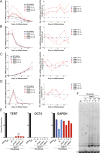

Comment in
-
Taking the brakes off telomerase.Elife. 2015 Jul 21;4:e09519. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09519. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26194808 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Taking the brakes off telomerase.Elife. 2015 Jul 21;4:e09519. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09519. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26194808 Free PMC article.
-
A novel two-step genome editing strategy with CRISPR-Cas9 provides new insights into telomerase action and TERT gene expression.Genome Biol. 2015 Nov 10;16:231. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0791-1. Genome Biol. 2015. PMID: 26553065 Free PMC article.
-
TERT promoter mutations in telomere biology.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;771:15-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28342451 Review.
-
Mutations in the promoter of the telomerase gene TERT contribute to tumorigenesis by a two-step mechanism.Science. 2017 Sep 29;357(6358):1416-1420. doi: 10.1126/science.aao0535. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Science. 2017. PMID: 28818973 Free PMC article.
-
TERT promoter mutations and telomeres during tumorigenesis.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Feb;60:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.02.001. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32163830 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing is a developmental switch for hTERT expression.Mol Cell. 2021 Jun 3;81(11):2349-2360.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.033. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33852895 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) histogram analysis to predict telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation status in glioblastoma.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jul 1;14(7):4840-4854. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-71. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39022283 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of the Noncoding Cancer Genome: A Target of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations.Cancer Discov. 2016 Nov;6(11):1215-1229. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0745. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27807102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TERT promoter C228T mutation in neural progenitors confers growth advantage following telomere shortening in vivo.Neuro Oncol. 2022 Dec 1;24(12):2063-2075. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noac080. Neuro Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35325218 Free PMC article.
-
PROBER identifies proteins associated with programmable sequence-specific DNA in living cells.Nat Methods. 2022 Aug;19(8):959-968. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01552-w. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Nat Methods. 2022. PMID: 35927480 Free PMC article.

