Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 26195256
- PMCID: PMC4694579
- DOI: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119
Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease
Erratum in
-
Clearance systems in the brain--implications for Alzheimer diseaser.Nat Rev Neurol. 2016 Apr;12(4):248. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.36. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27020556 No abstract available.
Abstract
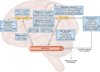
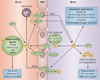
Accumulation of toxic protein aggregates-amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau tangles-is the pathological hallmark of Alzheimer disease (AD). Aβ accumulation has been hypothesized to result from an imbalance between Aβ production and clearance; indeed, Aβ clearance seems to be impaired in both early and late forms of AD. To develop efficient strategies to slow down or halt AD, it is critical to understand how Aβ is cleared from the brain. Extracellular Aβ deposits can be removed from the brain by various clearance systems, most importantly, transport across the blood-brain barrier. Findings from the past few years suggest that astroglial-mediated interstitial fluid (ISF) bulk flow, known as the glymphatic system, might contribute to a larger portion of extracellular Aβ (eAβ) clearance than previously thought. The meningeal lymphatic vessels, discovered in 2015, might provide another clearance route. Because these clearance systems act together to drive eAβ from the brain, any alteration to their function could contribute to AD. An understanding of Aβ clearance might provide strategies to reduce excess Aβ deposits and delay, or even prevent, disease onset. In this Review, we describe the clearance systems of the brain as they relate to proteins implicated in AD pathology, with the main focus on Aβ.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS028642/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020245/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL111724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118624/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL118624/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG012101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG008051/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG022374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS028642/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG20245/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG13616/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG12101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

