Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 26196006
- PMCID: PMC4506010
- DOI: 10.5812/ijp.425
Flixweed vs. Polyethylene Glycol in the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is often considered as the first-line treatment for functional constipation in children. Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb et Berth (D. sophia) is a safe recommended medicine in Iranian folk and Traditional Persian Medicine for the treatment of constipation.
Objectives: To clinically compare D. sophia with PEG 4000 (without electrolyte) in pediatric constipation and to assess its efficacy and side effects.
Patients and methods: 120 patients aged 2 - 12 years with constipation for at least 3 months were included in an 8 weeks lasting randomized controlled trial within two parallel-groups. Children received either PEG, 0.4 g/kg/day, or D. sophia seeds, 2 grams (for children aged 2 - 4 years) and 3 grams (for those aged > 4 years) per day.
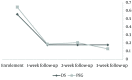
Results: A total of 109 patients completed the study (56 in D. sophia and 53 in PEG group). At the end of the study, 36 (64.3%) patients in D. sophia group and 29 (54.7%) in PEG group were out of Rome III criteria (P = 0.205). Median weekly stool frequency in 0, 1, 2, 3 weeks of the treatment was found to be 2, 5, 5, 5 in D. sophia and 3, 4, 4, 5 in PEG group (P = 0.139, 0.076, 0.844, 0.294), respectively. The number of patients who suffered flatulence was less (5, 8.9%) in D. sophia group as compared to PEG group (6, 11.3%) at the end of the trial (P = 0.461). D. sophia taste was less tolerated.
Conclusions: D. sophia is introduced as a cheap and available medication which can be applied as a safe alternative to conventional PEG in the management of pediatric chronic functional constipation.
Keywords: Children; Constipation; Descurainia Sophia; Polyethylene Glycol.
Figures
References
-
- Colonic Transit Time In 64 Iranian Patients With Idiopathic Chronic Constipation. Ansari R, Sohrabi MR, Roohi S, Mikaeli J, Massarrat S, Tahaghoghi Mehrizi S, et al. Arch Iran Med. 2001;4(1):6.
-
- Clinical Manifestations of Hirschsprung’ s Disease: A Six Year Course Review of Admitted Patients in Gilan, Northern Iran. Izadi M, Mansour-Ghanaei F, Jafarshad R, Joukar F, Bagherzadeh AH, Tareh F. Middle East J Digest Dis. 2009;1(2):68.
-
- Constipation in infants and children: evaluation and treatment. A medical position statement of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition. Baker SS, Liptak GS, Colletti RB, Croffie JM, Di Lorenzo C, Ector W, et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1999;29(5):612. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources