The enhanced inhibitory effect of different antitumor agents in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems on human cervical cancer HeLa cells
- PMID: 26197311
- PMCID: PMC6332159
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules200713226
The enhanced inhibitory effect of different antitumor agents in self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems on human cervical cancer HeLa cells
Abstract
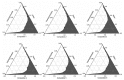
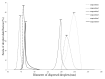
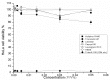
The aim of this study was to develop topical self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (SMEDDS) containing antitumor agents (bleomycin, cisplatin and ifosfamide) and to investigate their inhibitory potential in SMEDDS on human cervical cancer HeLa cells. The physicochemical properties of cytostatic drug loaded SMEDDS were characterized. The cytotoxicity of main components of SMEDDS was also investigated. Their IC50 values were determined. HeLa cells were treated by different concentrations of cisplatin, bleomycin and ifosfamide alone and in various SMEDDS. The inhibitory effect on cell growth was analyzed by MTT cell viability assay. Inflammation is a driving force that accelerates cancer development. The inhibitory effect of these antitumor agents has also been tested on HeLa cells in the presence of inflammatory mediators (IL-1-β, TNF-α) as an in vitro model of inflamed human cervix. Significant differences in the cytotoxicity of cytostatic drugs alone and in SMEDDS have been found in a concentration-dependent manner. The self-micro emulsifying system may potentiate the effectiveness of bleomycin, cisplatin and ifosfamide topically. The effect of SMEDDS containing antitumor agents was decreased significantly in the presence of inflammatory mediators. According to our experiments, the optimal SMEDDS formulation is 1:1:2:6:2 ratios of Isopropyl myristate, Capryol 90, Kolliphor RH 40, Cremophor RH40, Transcutol HP and Labrasol. It can be concluded that SMEDDS may increase the inhibitory effect of bleomycin, ifosfamide and cisplatin on human cervical cancer HeLa cells. Inflammation on HeLa cells hinders the effectiveness of SMEDDS containing antitumor agents. Our results might ensure useful data for development of optimal antitumor formulations.
Keywords: HeLa; SMEDDS; bleomycin; cisplatin; ifosfamide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Formulation and characetization of self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems according to their cytotoxic attributes].Acta Pharm Hung. 2014;84(2):69-76. Acta Pharm Hung. 2014. PMID: 25167702 Hungarian.
-
Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) improves anticancer effect of oral 9-nitrocamptothecin on human cancer xenografts in nude mice.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008 Aug;69(3):899-907. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.02.023. Epub 2008 Mar 8. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008. PMID: 18434109
-
A novel folate-modified self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of curcumin for colon targeting.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:151-62. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S27639. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22275831 Free PMC article.
-
Self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS)--challenges and road ahead.Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):675-90. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.896058. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24670091 Review.
-
Development of Drug Targeting and Delivery in Cervical Cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(8):792-806. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666171009165105. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29032751 Review.
Cited by
-
Metadata analysis to explore hub of the hub-genes highlighting their functions, pathways and regulators for cervical cancer diagnosis and therapies.Discov Oncol. 2022 Aug 22;13(1):79. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00546-6. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35994213 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a Vaginal Suppository Formulation to Deliver SHetA2 as a Novel Treatment for Cervical Dysplasia.J Pharm Sci. 2018 Feb;107(2):638-646. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.09.018. Epub 2017 Oct 6. J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 28989018 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic in vivo-like organotypic blood-brain barrier model to probe metastatic brain tumors.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 10;6:36670. doi: 10.1038/srep36670. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27830712 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating ifosfamide into salvia oil-based nanoemulsion diminishes its nephrotoxicity in mice inoculated with tumor.Bioimpacts. 2020;10(1):9-16. doi: 10.15171/bi.2020.02. Epub 2019 May 22. Bioimpacts. 2020. PMID: 31988852 Free PMC article.
-
Simplex Lattice Design and Machine Learning Methods for the Optimization of Novel Microemulsion Systems to Enhance p-Coumaric Acid Oral Bioavailability: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Mar 6;25(3):56. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02766-1. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38448576
References
-
- Rein D.T., Kurbacher C.M., Breidenbach M., Schöndorf T., Schmidt T., König E., Göhring U.J., Blohmer J.U., Mallman P. Weekly carboplatin and docetaxel for locally advanced primary and recurrent cervical cancer: A phase study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2002;87:98–103. doi: 10.1006/gyno.2002.6786. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herod J., Burton A., Buxton J., Tobias J., Luesley D., Jordan S., Dunn J., Poole C.J. A randomised, prospective, phase III clinical trial of primary bleomycin, ifosfamide and cisplatin (BIP) chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in inoperable cancer of the cervix. Ann. Oncol. 2000;11:1175–1181. doi: 10.1023/A:1008346901733. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

