Large-Scale and Comprehensive Immune Profiling and Functional Analysis of Normal Human Aging
- PMID: 26197454
- PMCID: PMC4509650
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133627
Large-Scale and Comprehensive Immune Profiling and Functional Analysis of Normal Human Aging
Abstract
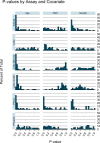
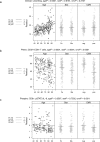
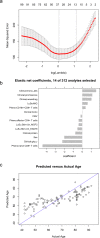
While many age-associated immune changes have been reported, a comprehensive set of metrics of immune aging is lacking. Here we report data from 243 healthy adults aged 40-97, for whom we measured clinical and functional parameters, serum cytokines, cytokines and gene expression in stimulated and unstimulated PBMC, PBMC phenotypes, and cytokine-stimulated pSTAT signaling in whole blood. Although highly heterogeneous across individuals, many of these assays revealed trends by age, sex, and CMV status, to greater or lesser degrees. Age, then sex and CMV status, showed the greatest impact on the immune system, as measured by the percentage of assay readouts with significant differences. An elastic net regression model could optimally predict age with 14 analytes from different assays. This reinforces the importance of multivariate analysis for defining a healthy immune system. These data provide a reference for others measuring immune parameters in older people.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Miller C, Kelsoe G (1995) Ig VH hypermutation is absent in the germinal centers of aged mice. J Immunol 155: 3377–3384. - PubMed
-
- Beerman I, Bhattacharya D, Zandi S, Sigvardsson M, Weissman IL, Bryder D, et al. (2010) Functionally distinct hematopoietic stem cells modulate hematopoietic lineage potential during aging by a mechanism of clonal expansion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107: 5465–5470. 10.1073/pnas.1000834107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA009302/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA194389/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI108906/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI057266/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042527/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC4AG039014/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI044142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC4 AG039014/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG045779/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117913/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI044142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI108891/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

