Identification of high-affinity VEGFR3-binding peptides through a phage-displayed random peptide library
- PMID: 26197772
- PMCID: PMC4620370
- DOI: 10.3802/jgo.2015.26.4.327
Identification of high-affinity VEGFR3-binding peptides through a phage-displayed random peptide library
Abstract
Objective: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) interaction with its receptor, VEGFR-3/Flt-4, regulates lymphangiogenesis. VEGFR-3/Flt-4 expression in cancer cells has been correlated with clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, and lymphatic invasion. The objective of this study is to identify a VEGFR-3/Flt-4-interacting peptide that could be used to inhibit VEGFR-3 for ovarian cancer therapy.
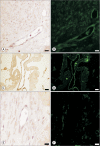
Methods: The extracellular fragment of recombinant human VEGFR-3/Flt-4 (rhVEGFR-3/Flt-4) fused with coat protein pIII was screened against a phage-displayed random peptide library. Using affinity enrichment and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) screening, positive clones of phages were amplified. Three phage clones were selected after four rounds of biopanning, and the specific binding of the peptides to rhVEGFR-3 was detected by ELISA and compared with that of VEGF-D. Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence analyses of ovarian cancer tissue sections was undertaken to demonstrate the specificity of the peptides.
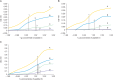
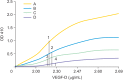
Results: After four rounds of biopanning, ELISA confirmed the specificity of the enriched bound phage clones for rhVEGFR-3. Sequencing and translation identified three different peptides. Non-competitive ELISA revealed that peptides I, II, and III had binding affinities for VEGFR-3 with K(aff) (affinity constant) of 16.4±8.6 μg/mL (n=3), 9.2±2.1 μg/mL (n=3), and 174.8±31.1 μg/mL (n=3), respectively. In ovarian carcinoma tissue sections, peptide III (WHWLPNLRHYAS), which had the greatest binding affinity, also co-localized with VEGFR-3 in endothelial cells lining lymphatic vessels; its labeling of ovarian tumors in vivo was also confirmed.
Conclusion: These finding showed that peptide III has high specificity and activity and, therefore, may represent a potential therapeutic approach to target VEGF-VEGFR-3 signaling for the treatment or diagnosis of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: Bacteriophages; Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay; Immunohistochemistry; Ovarian Neoplasms; Peptides; Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin. 2000;50:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R, Kaye SB. Ovarian cancer: strategies for overcoming resistance to chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:502–516. - PubMed
-
- Sant M, Allemani C, Santaquilani M, Knijn A, Marchesi F, Capocaccia R. EUROCARE-4. Survival of cancer patients diagnosed in 1995-1999. Results and commentary. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:931–991. - PubMed
-
- Al-Rawi MA, Mansel RE, Jiang WG. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005;31:117–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

