Robotic high para-aortic lymph node dissection with high port placement using same port for pelvic surgery in gynecologic cancer patients
- PMID: 26197858
- PMCID: PMC4510339
- DOI: 10.3802/jgo.2015.26.3.222
Robotic high para-aortic lymph node dissection with high port placement using same port for pelvic surgery in gynecologic cancer patients
Abstract
Objective: This study reports our initial experience of robotic high para-aortic lymph node dissection (PALND) with high port placement using same port for pelvic surgery in cervical and endometrial cancer patients.
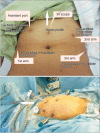
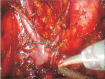
Methods: Between July 2013 and January 2014, we performed robotic high PALND up to the left renal vein during staging surgeries. With high port placement and same port usage for pelvic surgery, high PALND was successfully performed without repositioning the robotic column. All data were registered consecutively and analyzed retrospectively.
Results: All patients successfully underwent robotic high PALND, followed by hysterectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection. Median age was 45 years (range, 39 to 51 years) and median body mass index was 22 kg/m² (range, 19.3 to 23.1 kg/m²). Median operative time for right PALND and left PALND was 37 minutes (range, 22 to 65 minutes) and 44 minutes (range, 36 to 50 minutes), respectively. Median number of right and left para-aortic lymph node by pathologic report was 12 (range, 8 to 15) and 13 (range, 5 to 26).
Conclusion: With high port placement and one assistant port, robotic high PALND with the same port used in pelvic surgery is feasible to non-obese patients.
Keywords: Endometrial Neoplasms; Intraoperative Complications; Lymph Node Excision; Robotics; Surgical Instruments; Uterine Cervical Neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Robot-assisted laparoscopic transperitoneal infrarenal lymphadenectomy in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer by single docking: Do we need a backup procedure?J Robot Surg. 2018 Mar;12(1):49-58. doi: 10.1007/s11701-017-0685-1. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Robot Surg. 2018. PMID: 28255734
-
Improving Double Docking for Robot-assisted Para-aortic Lymphadenectomy in Endometrial Cancer Staging: Technique and Surgical Outcomes.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016 Jul-Aug;23(5):818-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2016.03.023. Epub 2016 Apr 8. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2016. PMID: 27063093
-
Learning curve and surgical outcome for robotic-assisted hysterectomy with lymphadenectomy: case-matched controlled comparison with laparoscopy and laparotomy for treatment of endometrial cancer.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010 Nov-Dec;17(6):739-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2010.07.008. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2010. PMID: 20955983
-
Indications and techniques for robotic pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy in gynecologic oncology.J Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;112(7):782-9. doi: 10.1002/jso.24005. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26288990 Review.
-
Indications and techniques for robotic pelvic and para-aortic lymphadenectomy with sentinel lymph node mapping in gynecologic oncology.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017 Nov;45:83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2017.04.006. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017. PMID: 28533155 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between Obesity, Surgical Route, and Perioperative Outcomes in Patients with Uterine Cancer.Minim Invasive Surg. 2018 Jun 19;2018:5130856. doi: 10.1155/2018/5130856. eCollection 2018. Minim Invasive Surg. 2018. PMID: 30018822 Free PMC article.
-
Oncologic and Operative Outcomes of Robotic Staging Surgery Using Low Pelvic Port Placement in High-Risk Endometrial Cancer.Curr Oncol. 2024 Dec 5;31(12):7820-7827. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31120576. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39727699 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic lower pelvic port placement for optimal upper paraaortic lymph node dissection.J Gynecol Oncol. 2018 Nov;29(6):e87. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2018.29.e87. J Gynecol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30207095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Possover M, Krause N, Plaul K, Kuhne-Heid R, Schneider A. Laparoscopic para-aortic and pelvic lymphadenectomy: experience with 150 patients and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 1998;71:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Kjorstad KE, Kolbenstvedt A, Strickert T. The value of complete lymphadenectomy in radical treatment of cancer of the cervix, stage IB. Cancer. 1984;54:2215–2219. - PubMed
-
- Magrina JF, Long JB, Kho RM, Giles DL, Montero RP, Magtibay PM. Robotic transperitoneal infrarenal aortic lymphadenectomy: technique and results. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2010;20:184–187. - PubMed
-
- Magrina JF, Kho R, Montero RP, Magtibay PM, Pawlina W. Robotic extraperitoneal aortic lymphadenectomy: development of a technique. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:32–35. - PubMed
-
- Jacob KA, Zanagnolo V, Magrina JF, Magtibay PM. Robotic transperitoneal infrarenal aortic lymphadenectomy for gynecologic malignancy: a left lateral approach. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2011;21:733–736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

