Advancing implementation science through measure development and evaluation: a study protocol
- PMID: 26197880
- PMCID: PMC4511441
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-015-0287-0
Advancing implementation science through measure development and evaluation: a study protocol
Abstract
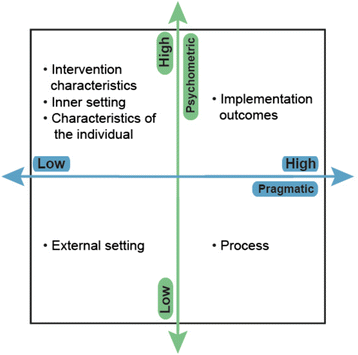
Background: Significant gaps related to measurement issues are among the most critical barriers to advancing implementation science. Three issues motivated the study aims: (a) the lack of stakeholder involvement in defining pragmatic measure qualities; (b) the dearth of measures, particularly for implementation outcomes; and (c) unknown psychometric and pragmatic strength of existing measures. Aim 1: Establish a stakeholder-driven operationalization of pragmatic measures and develop reliable, valid rating criteria for assessing the construct. Aim 2: Develop reliable, valid, and pragmatic measures of three critical implementation outcomes, acceptability, appropriateness, and feasibility. Aim 3: Identify Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research and Implementation Outcome Framework-linked measures that demonstrate both psychometric and pragmatic strength.
Methods/design: For Aim 1, we will conduct (a) interviews with stakeholder panelists (N = 7) and complete a literature review to populate pragmatic measure construct criteria, (b) Q-sort activities (N = 20) to clarify the internal structure of the definition, (c) Delphi activities (N = 20) to achieve consensus on the dimension priorities, (d) test-retest and inter-rater reliability assessments of the emergent rating system, and (e) known-groups validity testing of the top three prioritized pragmatic criteria. For Aim 2, our systematic development process involves domain delineation, item generation, substantive validity assessment, structural validity assessment, reliability assessment, and predictive validity assessment. We will also assess discriminant validity, known-groups validity, structural invariance, sensitivity to change, and other pragmatic features. For Aim 3, we will refine our established evidence-based assessment (EBA) criteria, extract the relevant data from the literature, rate each measure using the EBA criteria, and summarize the data.
Discussion: The study outputs of each aim are expected to have a positive impact as they will establish and guide a comprehensive measurement-focused research agenda for implementation science and provide empirically supported measures, tools, and methods for accomplishing this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical