Cis- and trans-regulation in X inactivation
- PMID: 26198462
- PMCID: PMC4761001
- DOI: 10.1007/s00412-015-0525-x
Cis- and trans-regulation in X inactivation
Abstract
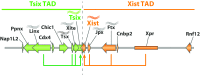
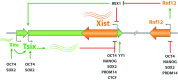
Female mammalian cells compensate dosage of X-linked gene expression through the inactivation of one of their two X chromosomes. X chromosome inactivation (XCI) in eutherians is dependent on the non-coding RNA Xist that is up-regulated from the future inactive X chromosome, coating it and recruiting factors involved in silencing and altering its chromatin state. Xist lies within the X-inactivation center (Xic), a region on the X that is required for XCI, and is regulated in cis by elements on the X chromosome and in trans by diffusible factors. In this review, we summarize the latest results in cis- and trans-regulation of the Xic. We discuss how the organization of the Xic in topologically associating domains is important for XCI (cis-regulation) and how proteins in the pluripotent state and upon development or differentiation of embryonic stem cells control proper inactivation of one X chromosome (trans-regulation).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The trans-activator RNF12 and cis-acting elements effectuate X chromosome inactivation independent of X-pairing.Mol Cell. 2014 Mar 20;53(6):965-78. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24613346
-
Long Noncoding RNAs and X Chromosome Inactivation.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2011;51:43-64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-16502-3_3. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21287133
-
X chromosome inactivation in a female carrier of a 1.28 Mb deletion encompassing the human X inactivation centre.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017 Nov 5;372(1733):20160359. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0359. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28947658 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interplay and function of multiple noncoding genes governing X chromosome inactivation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1859(1):112-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26260844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function and evolution of the long noncoding RNA circuitry orchestrating X-chromosome inactivation in mammals.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016 Sep;7(5):702-22. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1359. Epub 2016 May 13. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016. PMID: 27173581 Review.
Cited by
-
Chd8 regulates X chromosome inactivation in mouse through fine-tuning control of Xist expression.Commun Biol. 2021 Apr 15;4(1):485. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-01945-1. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 33859315 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of X-linked gene expression during early mouse development by Rlim.Elife. 2016 Sep 19;5:e19127. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19127. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27642011 Free PMC article.
-
The "lnc" between 3D chromatin structure and X chromosome inactivation.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:35-47. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27062886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spindle tubulin and MTOC asymmetries may explain meiotic drive in oocytes.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 27;9(1):2952. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05338-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30054463 Free PMC article.
-
Derivation of a minimal functional XIST by combining human and mouse interaction domains.Hum Mol Genet. 2023 Apr 6;32(8):1289-1300. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac285. Hum Mol Genet. 2023. PMID: 36426827 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

