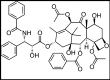
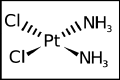
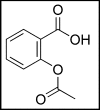
The in vitro protective effect of salicylic acid against paclitaxel and cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity
- PMID: 26199062
- PMCID: PMC4960183
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-015-9896-3
The in vitro protective effect of salicylic acid against paclitaxel and cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity
Abstract
Paclitaxel (PAC) and cisplatin (CIS) are two established chemotherapeutic drugs used in combination for the treatment of various solid tumors. However, the usage of PAC and CIS are limited because of the incidence of their moderate or severe neurotoxic side effects. In this study, we aimed to assess the protective role of salicylic acid (SA) against neurotoxicity caused by PAC and CIS. For this purpose, newborn Sprague Dawley rats were decapitated in sterile atmosphere and primary cortex neuron cultures were established. On the 10th day SA was added into culture plates. PAC and CIS were added on the 12th day. The cytotoxicity was determined by using the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay. Oxidative alterations were assessed using total antioxidant capacity and total oxidative stress assays in rat primary neuron cell cultures. It was shown that both concentrations of PAC and CIS treatments caused neurotoxicity. Although SA decreased the neurotoxicity by CIS and PAC, it was more effective against the toxicity caused by CIS rather than the toxicity caused by PAC. In conclusion it was clearly revealed that SA decreased the neurotoxic effect of CIS and PAC in vitro.
Keywords: Antioxidant capacity; Cisplatin; Neurotoxicity; Oxidative stress; Paclitaxel; Salicylic acid.
Figures
References
-
- Chen C, Bai X, Bi Y, Liu G, Li H, Liu Z, Liu H (2015) Insulin-like growth factor-1 attenuates apoptosis and protects neurochemical phenotypes of dorsal root ganglion neurons with paclitaxel-induced neurotoxicity in vitro. Nutr Neurosci. doi:10.1179/1476830514Y.0000000147 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources