Strategic Use of Telescopic Retainers and Semi-rigid Precision Attachments in a Geriatric Patient: A Case Report
- PMID: 26199522
- PMCID: PMC4501977
- DOI: 10.1007/s13191-013-0302-6
Strategic Use of Telescopic Retainers and Semi-rigid Precision Attachments in a Geriatric Patient: A Case Report
Abstract
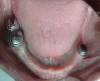
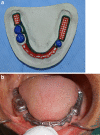
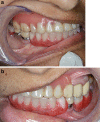
The rehabilitation of medically compromised elderly patients with long span partially edentulous arches has been a tremendous challenge for dentists. Proper dental management requires a commitment to provide the best treatment despite the compromised oral conditions. The aim of this paper is to describe the prosthetic rehabilitation of an elderly patient who presented with chief complaints of gagging sensation while using upper denture, loose upper and lower dentures and difficulty in eating food. Patient was rehabilitated using removable partial denture with semi-rigid attachments in the maxillary arch and telescopic prosthesis in the mandibular arch. Use of semi precision attachments helped in increasing the retentive ability of the maxillary prosthesis, even in the presence of only few abutments. Fabrication of a telescopic denture is a technique sensitive procedure but it offers advantages like bilateral splinting effect in long span partially edentulous arches, reduced effective crown-root ratio, maintenance of proprioception and transfer of forces along the long axis of the abutments. Although the management was complex but it improved patient's esthetics, oral function and social confidence.
Keywords: Fixed removable prosthesis; Multiple missing teeth; Semi-precision attachment; Telescopic prosthesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unique, Cost-effective and Retentive Removable Prosthesis to Rehabilitate Long Span Kennedy's Class I Edentulism with Custom Attachment System: A Case Report.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2020 Feb 1;21(2):215-218. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2020. PMID: 32381831
-
Telescopic overdenture for oral rehabilitation of ectodermal dysplasia patient.Contemp Clin Dent. 2015 Sep;6(Suppl 1):S258-61. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.166821. Contemp Clin Dent. 2015. PMID: 26604583 Free PMC article.
-
Stress distribution of abutments and base displacement with precision attachment- and telescopic crown-retained removable partial dentures.J Oral Rehabil. 2003 May;30(5):482-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2003.01092.x. J Oral Rehabil. 2003. PMID: 12752927
-
Telescopic crown-retained removable partial dentures: review and case report.Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2001 Nov;22(11):927-8, 929-32, 934 passim; quiz 942. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2001. PMID: 11803658 Review.
-
[(Semi-)precision attachments for cast metal frame removable partial dentures].Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2011 Feb;118(2):93-100. doi: 10.5177/ntvt.2011.02.10290. Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2011. PMID: 21438359 Review. Dutch.
Cited by
-
Ten-year clinical performance of non-precious metal double crowns with friction pins in severely reduced dentitions-a retrospective study.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Apr;27(4):1623-1635. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04788-0. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 36414766 Free PMC article.
-
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of a Patient with Missing Teeth and Loss of Vertical Dimension Using Telescopic Overdentures.Contemp Clin Dent. 2021 Jan-Mar;12(1):67-72. doi: 10.4103/ccd.ccd_191_20. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Contemp Clin Dent. 2021. PMID: 33967541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eichner K. Recent knowledge gained from long-term observations in the field of prosthodontics. Int Dent J. 1984;34:35–40. - PubMed
-
- Ante IH. The fundamental principles, design and construction of crown and bridge prosthesis. Dent Items Interest. 1928;1:215–232.
-
- Misch CE. Dental implant prosthetics. 2. St Louis: Elsevier Mosby; 2005. p. 207.
-
- Swoope CC. Prosthetic considerations in tooth removal. Dent Clin North Am. 1969;13:857–870. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
