Delayed hippocampal neuronal death in young gerbil following transient global cerebral ischemia is related to higher and longer-term expression of p63 in the ischemic hippocampus
- PMID: 26199612
- PMCID: PMC4498357
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.158359
Delayed hippocampal neuronal death in young gerbil following transient global cerebral ischemia is related to higher and longer-term expression of p63 in the ischemic hippocampus
Abstract
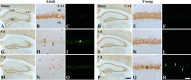
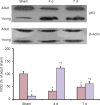
The tumor suppressor p63 is one of p53 family members and plays a vital role as a regulator of neuronal apoptosis in the development of the nervous system. However, the role of p63 in mature neuronal death has not been addressed yet. In this study, we first compared ischemia-induced effects on p63 expression in the hippocampal regions (CA1-3) between the young and adult gerbils subjected to 5 minutes of transient global cerebral ischemia. Neuronal death in the hippocampal CA1 region of young gerbils was significantly slow compared with that in the adult gerbils after transient global cerebral ischemia. p63 immunoreactivity in the hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in the sham-operated young group was significantly low compared with that in the sham-operated adult group. p63 immunoreactivity was apparently changed in ischemic hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in both ischemia-operated young and adult groups. In the ischemia-operated adult groups, p63 immunoreactivity in the hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons was significantly decreased at 4 days post-ischemia; however, p63 immunoreactivity in the ischemia-operated young group was significantly higher than that in the ischemia-operated adult group. At 7 days post-ischemia, p63 immunoreactivity was decreased in the hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in both ischemia-operated young and adult groups. Change patterns of p63 level in the hippocampal CA1 region of adult and young gerbils after ischemic damage were similar to those observed in the immunohistochemical results. These findings indicate that higher and longer-term expression of p63 in the hippocampal CA1 region of the young gerbils after ischemia/reperfusion may be related to more delayed neuronal death compared to that in the adults.
Keywords: CA1 region; cerebral ischemia/reperfusion; delayed neuronal death; immunohistochemistry; neural regeneration; p53 tumor suppressor gene family; pyramidal neurons; western blotting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differences in TNF‑α and TNF‑R1 expression in damaged neurons and activated astrocytes of the hippocampal CA1 region between young and adult gerbils following transient forebrain ischemia.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):625. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12264. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34212986 Free PMC article.
-
p63 Expression in the Gerbil Hippocampus Following Transient Ischemia and Effect of Ischemic Preconditioning on p63 Expression in the Ischemic Hippocampus.Neurochem Res. 2015 May;40(5):1013-22. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1556-7. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 25777256
-
Effects of ischemic preconditioning on VEGF and pFlk-1 immunoreactivities in the gerbil ischemic hippocampus after transient cerebral ischemia.J Neurol Sci. 2014 Dec 15;347(1-2):179-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.09.044. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25300771
-
Differences in the protein expression levels of Trx2 and Prx3 in the hippocampal CA1 region between adult and aged gerbils following transient global cerebral ischemia.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):2555-62. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3760. Epub 2015 May 8. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25955690 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection of antioxidant enzymes against transient global cerebral ischemia in gerbils.Anat Cell Biol. 2014 Sep;47(3):149-56. doi: 10.5115/acb.2014.47.3.149. Epub 2014 Sep 23. Anat Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25276473 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age-dependent changes of p53 and p63 immunoreactivities in the mouse hippocampus.Lab Anim Res. 2019 Oct 29;35:20. doi: 10.1186/s42826-019-0022-0. eCollection 2019. Lab Anim Res. 2019. PMID: 32257908 Free PMC article.
-
Ferulic acid exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in vitro and in vivo.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Nov;40(5):1444-1456. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3127. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28901374 Free PMC article.
-
Less hippocampal neuronal death in young gerbils following transient global cerebral ischemia is associated with long‑term maintenance of insulin‑like growth factor 1 and its receptors in the hippocampal CA1 region.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Feb;17(2):3055-3061. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8243. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29257289 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ischemic preconditioning on PDGF-BB expression in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region following transient cerebral ischemia.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):1627-1634. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6799. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28627606 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in TNF‑α and TNF‑R1 expression in damaged neurons and activated astrocytes of the hippocampal CA1 region between young and adult gerbils following transient forebrain ischemia.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):625. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12264. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34212986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An SJ, Kang TC, Park SK, Hwang IK, Cho SS, Chung MH, Won MH. Oxidative DNA damage and alteration of glutamate transporter expressions in the hippocampal CA1 area immediately after ischemic insult. Mol Cells. 2002;13:476–480. - PubMed
-
- Banasiak KJ, Haddad GG. Hypoxia-induced apoptosis: effect of hypoxic severity and role of p53 in neuronal cell death. Brain Res. 1998;797:295–304. - PubMed
-
- Bertolino G, De Araujo FL, Souza HC, Coimbra NC, De Araujo JE. Neuropathology and behavioral impairments after bilateral global ischemia surgery and exposure to static magnetic field: Evidence in the motor cortex, the hippocampal CA1 region and the neostriatum. Int J Radiat Biol. 2013;89:595–601. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand N, Ishii H, Spatz M. Cerebral ischemia in young and adult gerbils: effects on cholinergic metabolism. Neurochem Int. 1996;28:293–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
