Quetiapine versus aripiprazole in the management of schizophrenia
- PMID: 26199719
- PMCID: PMC4502587
- DOI: 10.1177/2045125315579870
Quetiapine versus aripiprazole in the management of schizophrenia
Abstract
Objectives: Current evidence supports the use of various second-generation antipsychotics for pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia. While in a systematic review, generally no difference in efficacy was found between atypical antipsychotics, other studies have found quetiapine less effective than aripiprazole. This article reviews the efficacy and tolerability of aripiprazole versus quetiapine in the context of recommended management strategies for schizophrenia.
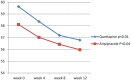
Method: Fifty female inpatients, meeting the diagnosis of schizophrenia, were randomly entered into two groups (n = 25 in each group) to participate in a 12-week, double-blind study for random assignment to quetiapine or aripiprazole. The primary outcome measures were Scale for Assessment of Positive Symptoms and Scale for Assessment of Negative Symptoms. The schedule for Assessment of Insight (SAI), Clinical Global Impressions Severity Scale (CGI-S) and the Simpson Angus Scale (SAS) were also used as secondary measures.
Results: Both quetiapine and aripiprazole showed significant effectiveness in the improvement of positive symptoms. The effectiveness for negative symptoms was also noteworthy with both drugs, although not to a significant level during this study. In addition, significant improvement was found on assessment with CGI-S and SAI for quetiapine and aripiprazole. SAS did not show any important increment in extrapyramidal side effects at the end of the examination.
Conclusion: According to the findings, quetiapine and aripiprazole had similar effectiveness and tolerability with respect to management of schizophrenia.
Keywords: aripiprazole; quetiapine; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multicentre, randomized, naturalistic, open-label study between aripiprazole and standard of care in the management of community-treated schizophrenic patients Schizophrenia Trial of Aripiprazole: (STAR) study.Eur Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;22(7):433-43. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.03.002. Epub 2007 Jun 7. Eur Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17555947 Clinical Trial.
-
Quetiapine extended release versus aripiprazole in children and adolescents with first-episode psychosis: the multicentre, double-blind, randomised tolerability and efficacy of antipsychotics (TEA) trial.Lancet Psychiatry. 2017 Aug;4(8):605-618. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(17)30166-9. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Lancet Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28599949 Clinical Trial.
-
Rapid versus conventional initiation of quetiapine in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, parallel-group trial.J Clin Psychiatry. 2007 Mar;68(3):399-405. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v68n0307. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17388709 Clinical Trial.
-
An open, large, 6-month naturalistic study of outcome in schizophrenic outpatients, treated with olanzapine.Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011 Jan;26(1):81-5. doi: 10.1002/hup.1173. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 23055416 Review.
-
Aripiprazole in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: A review.Clin Ther. 2010;32 Suppl 1:S3-20. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.01.021. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20152550 Review.
Cited by
-
Updating the Comparative Evidence on Second-Generation Antipsychotic Use With Schizophrenia.Psychiatr Res Clin Pract. 2020 Oct 16;2(2):76-87. doi: 10.1176/appi.prcp.20200004. eCollection 2020 Dec. Psychiatr Res Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 36101867 Free PMC article.
-
Brexpiprazole Attenuates Aggression, Suicidality and Substance Use in Borderline Personality Disorder: A Case Series.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Feb 7;60(2):283. doi: 10.3390/medicina60020283. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38399570 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of rivastigmine on positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia: a double-blind clinical trial.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016 Oct;6(5):308-316. doi: 10.1177/2045125316656334. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27721970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreasen N. (1981) The Scale for Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS). Iowa City, IA: Department of Psychiatry, University of Iowa.
-
- Andreasen N. (1984) The Scale for Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS).
-
- APA (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Citrome L. (2012) A systematic review of meta-analyses of the efficacy of oral atypical antipsychotics for the treatment of adult patients with schizophrenia. Exp Opin Pharmacother 13: 1545–1573. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources