Transplantation of Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Platelet-Rich Plasma Accelerate Distraction Osteogenesis in A Canine Model
- PMID: 26199903
- PMCID: PMC4503838
- DOI: 10.22074/cellj.2016.3724
Transplantation of Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Platelet-Rich Plasma Accelerate Distraction Osteogenesis in A Canine Model
Abstract
Objective: Distraction osteogenesis (DO) is a surgical procedure used to generate large volumes of new bone for limb lengthening.
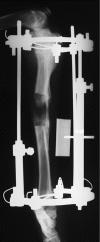
Materials and methods: In this animal experimental study, a 30% lengthening of the left tibia (mean distraction distance: 60.8 mm) was performed in ten adult male dogs by callus distraction after osteotomy and application of an Ilizarov fixator. Distraction was started on postoperative day seven with a distraction rate of 0.5 mm twice per day and carried out at a rate of 1.5 mm per day until the end of the study. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) as the treatment group (n=5) or PRP alone (control group, n=5) were injected into the distracted callus at the middle and end of the distraction period. At the end of the consolidation period, the dogs were sacrificed after which computerized tomography (CT) and histomorphometric evaluations were performed.
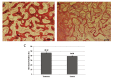
Results: Radiographic evaluationsrevealed that the amount and quality of callus formations were significantly higher in the treatment group (P<0.05). As measured by CT scan, the healing parametersin dogs of the treatment group were significantly greater (P<0.05). New bone formation in the treatment group was significantly higher (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The present study showed that the transplantation of BM-MSCs positively affects early bony consolidation in DO. The use of MSCs might allow a shortened period of consolidation and therefore permit earlier device removal.
Keywords: Autologous Transplantation; Bone Lengthening; Distraction Osteogenesis; Mesenchymal Stem Cells; Platelet-Rich Plasma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bone marrow aspirate concentrate and platelet-rich plasma enhanced bone healing in distraction osteogenesis of the tibia.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014 Dec;472(12):3789-97. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3548-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014. PMID: 24599650 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Administration of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells in lengthening phase accelerates early bone consolidation in rat distraction osteogenesis model.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Mar 20;11(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01635-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32197646 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma during distraction osteogenesis--a preliminary result of three cases.Bone. 2004 Oct;35(4):892-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2004.06.013. Bone. 2004. PMID: 15454096
-
Role of distraction osteogenesis in craniomaxillofacial surgery.Innov Surg Sci. 2016 Dec 8;1(2):97-103. doi: 10.1515/iss-2016-0027. eCollection 2016 Dec. Innov Surg Sci. 2016. PMID: 31579725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of bone lengthening.J Child Orthop. 2016 Dec;10(6):487-492. doi: 10.1007/s11832-016-0780-2. Epub 2016 Nov 12. J Child Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27838825 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet Function and Therapeutic Applications in Dogs: Current Status and Future Prospects.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jan 25;10(2):201. doi: 10.3390/ani10020201. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31991713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombin-activated platelet-rich plasma enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by activating SIRT1-mediated autophagy.Eur J Med Res. 2021 Sep 15;26(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s40001-021-00575-x. Eur J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34526113 Free PMC article.
-
Platet Rich Plasma or Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy as callus accellerator in aseptic tibial non union. Evaluate of outcomes.Acta Biomed. 2020 Nov 10;91(4):e2020188. doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i4.8818. Acta Biomed. 2020. PMID: 33525281 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of bone regeneration in mandible large defect using undifferentiated adipose stem cells loaded on gelatin carrier: An animal model case study.J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021 Winter;15(1):22-29. doi: 10.34172/joddd.2021.005. Epub 2021 Feb 13. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021. PMID: 33927837 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine tongue epithelium-derived cells: A new source of bovine mesenchymal stem cells.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20181829. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181829. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32232387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ilizarov GA. The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissues.Part I.The influence of stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(238):249–281. - PubMed
-
- Feng X, Tuo X, Chen F, Wu W, Ding Y, Duan Y, et al. Ultrastructural cell response to tension stress during mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(7):527–532. - PubMed
-
- Codivilla A. On the means of lengthening, in the lower limbs, the muscles and tissues which are shortened through deformity. Am J Orthop Surg. 1905;2:353–363.
-
- Ilizarov GA. Clinical application of the tension-stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(250):8–26. - PubMed
-
- Kinoshita K, Hibi H, Yamada Y, Ueda M. Promoted new bone formation in Maxillary distraction osteogenesis using a tissue-engineered osteogenic material. J Craniofac Surg. 2008;19(1):80–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
