Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser
- PMID: 26200343
- PMCID: PMC4521999
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14656
Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin by femtosecond X-ray laser
Abstract
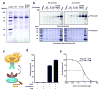
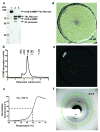
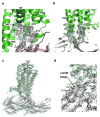
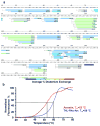
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) signal primarily through G proteins or arrestins. Arrestin binding to GPCRs blocks G protein interaction and redirects signalling to numerous G-protein-independent pathways. Here we report the crystal structure of a constitutively active form of human rhodopsin bound to a pre-activated form of the mouse visual arrestin, determined by serial femtosecond X-ray laser crystallography. Together with extensive biochemical and mutagenesis data, the structure reveals an overall architecture of the rhodopsin-arrestin assembly in which rhodopsin uses distinct structural elements, including transmembrane helix 7 and helix 8, to recruit arrestin. Correspondingly, arrestin adopts the pre-activated conformation, with a ∼20° rotation between the amino and carboxy domains, which opens up a cleft in arrestin to accommodate a short helix formed by the second intracellular loop of rhodopsin. This structure provides a basis for understanding GPCR-mediated arrestin-biased signalling and demonstrates the power of X-ray lasers for advancing the frontiers of structural biology.
Figures



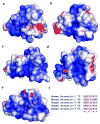
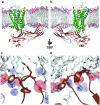
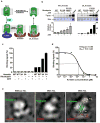
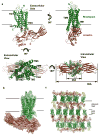
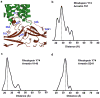
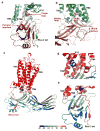


Comment in
-
Structural biology: Arresting developments in receptor signalling.Nature. 2015 Jul 30;523(7562):538-9. doi: 10.1038/nature14637. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26200346 No abstract available.
-
X-ray computed tomography datasets for forensic analysis of vertebrate fossils.Sci Data. 2016 Jun 7;3:160040. doi: 10.1038/sdata.2016.40. Sci Data. 2016. PMID: 27272251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilden U, Hall SW, Kuhn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1986;83:1174–1178. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 DK066202/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM097463/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM094599/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK071662/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103310/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM073197/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM077561/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097463/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM095583/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM109955/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM094586/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY000331/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY011500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM073197/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM094618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY005216/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM102545/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM095583/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071662/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM104212/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM103310/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM108635/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM077561/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EY005216/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY011500/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM073210/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM087413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM104212/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027270/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30EY000331/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- GM108635/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM102545/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

