227 Views of RNA: Is RNA Unique in Its Chemical Isomer Space?
- PMID: 26200431
- PMCID: PMC4523004
- DOI: 10.1089/ast.2014.1213
227 Views of RNA: Is RNA Unique in Its Chemical Isomer Space?
Abstract
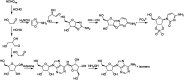
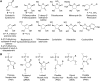
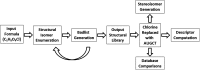
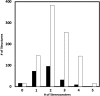
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is one of the two nucleic acids used by extant biochemistry and plays a central role as the intermediary carrier of genetic information in transcription and translation. If RNA was involved in the origin of life, it should have a facile prebiotic synthesis. A wide variety of such syntheses have been explored. However, to date no one-pot reaction has been shown capable of yielding RNA monomers from likely prebiotically abundant starting materials, though this does not rule out the possibility that simpler, more easily prebiotically accessible nucleic acids may have preceded RNA. Given structural constraints, such as the ability to form complementary base pairs and a linear covalent polymer, a variety of structural isomers of RNA could potentially function as genetic platforms. By using structure-generation software, all the potential structural isomers of the ribosides (BC5H9O4, where B is nucleobase), as well as a set of simpler minimal analogues derived from them, that can potentially serve as monomeric building blocks of nucleic acid-like molecules are enumerated. Molecules are selected based on their likely stability under biochemically relevant conditions (e.g., moderate pH and temperature) and the presence of at least two functional groups allowing the monomers to be incorporated into linear polymers. The resulting structures are then evaluated by using molecular descriptors typically applied in quantitative structure-property relationship (QSPR) studies and predicted physicochemical properties. Several databases have been queried to determine whether any of the computed isomers had been synthesized previously. Very few of the molecules that emerge from this structure set have been previously described. We conclude that ribonucleosides may have competed with a multitude of alternative structures whose potential proto-biochemical roles and abiotic syntheses remain to be explored.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Structural and electronic properties of barbituric acid and melamine-containing ribonucleosides as plausible components of prebiotic RNA: implications for prebiotic self-assembly.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017 Nov 22;19(45):30762-30771. doi: 10.1039/c7cp06123d. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017. PMID: 29165453
-
Synthesis of fluorinated indoles as RNA analogues.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2007;26(8-9):869-71. doi: 10.1080/15257770701505220. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2007. PMID: 18058498
-
Asphalt, water, and the prebiotic synthesis of ribose, ribonucleosides, and RNA.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Dec 18;45(12):2025-34. doi: 10.1021/ar200332w. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22455515
-
Abiotic synthesis of RNA in water: a common goal of prebiotic chemistry and bottom-up synthetic biology.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014 Oct;22:146-57. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2014.09.015. Epub 2014 Oct 25. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25438801 Review.
-
Isostericity and tautomerism of base pairs in nucleic acids.FEBS Lett. 2014 Aug 1;588(15):2464-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.06.031. Epub 2014 Jun 17. FEBS Lett. 2014. PMID: 24950426 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring astrobiology using in silico molecular structure generation.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017 Dec 28;375(2109):20160344. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2016.0344. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017. PMID: 29133444 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics as an Emerging Tool in the Search for Astrobiologically Relevant Biomarkers.Astrobiology. 2020 Oct;20(10):1251-1261. doi: 10.1089/ast.2019.2135. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Astrobiology. 2020. PMID: 32551936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolvability Is an Evolved Ability: The Coding Concept as the Arch-Unit of Natural Selection.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2016 Mar;46(1):67-79. doi: 10.1007/s11084-015-9464-z. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2016. PMID: 26419865
-
Hidden Concepts in the History and Philosophy of Origins-of-Life Studies: a Workshop Report.Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2019 Sep;49(3):111-145. doi: 10.1007/s11084-019-09580-x. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Orig Life Evol Biosph. 2019. PMID: 31399826 Review.
-
Deciphering Biosignatures in Planetary Contexts.Astrobiology. 2019 Sep;19(9):1075-1102. doi: 10.1089/ast.2018.1903. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Astrobiology. 2019. PMID: 31335163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agrofoglio L., and Challand S.R. (1998) Acyclic, Carbocyclic and L-Nucleosides, Springer, Dordrecht, the Netherlands
-
- Bean H.D., Anet F.A., Gould I.R., and Hud N.V. (2006) Glyoxylate as a backbone linkage for a prebiotic ancestor of RNA. Orig Life Evol Biosph 36:39–63 - PubMed
-
- Bean H.D., Sheng Y., Collins J.P., Anet F.A., Leszczynski J., and Hud N.V. (2007) Formation of a beta-pyrimidine nucleoside by a free pyrimidine base and ribose in a plausible prebiotic reaction. J Am Chem Soc 129:9556–9557 - PubMed
-
- Beck A., Lohrmann R., and Orgel L.E. (1967) Phosphorylation with inorganic phosphates at moderate temperatures. Science 157:952. - PubMed
-
- Benner S.A. (1999) How small can a microorganism be? In Size Limits of Very Small Microorganisms: Proceedings of a Workshop, Steering Group for the Workshop on Size Limits of Very Small Microorganisms, Space Studies Board, National Academies Press, Washington, DC, pp 126–138
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
