Accuracy of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Quantifying Acute Kidney Injury after Partial Nephrectomy in Patients with Normal Contralateral Kidney
- PMID: 26200468
- PMCID: PMC4511768
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133675
Accuracy of Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Quantifying Acute Kidney Injury after Partial Nephrectomy in Patients with Normal Contralateral Kidney
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the efficacy of urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) for predicting the degree of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients following partial nephrectomy (PN).
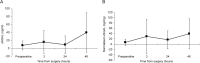
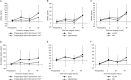
Methods: This prospective study included 176 patients who underwent open or laparoscopic PN for solid renal tumors between June 2013 and May 2014. Urine samples were collected preoperatively and at 3, 24, and 48 h after renal pedicle clamp removal. Changes in uNGAL levels were analyzed for all patients and between subgroups that were dichotomized based on preoperative eGFR values of <60 and ≥60 mL/min/1.73m2, open and laparoscopic surgery, and according to the onset of AKI. Linear mixed models were used to investigate preoperative and perioperative features associated with postoperative uNGAL and eGFR changes at 6 months postoperatively.
Results: Among 146 patients included in the final analysis, 10 (6.8%) patients had preoperative eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73m2. In the overall group, uNGAL levels increased following PN. However, all subgroups demonstrated comparable changes in uNGAL levels over time. Multivariate analyses failed to reveal any correctable clinical features associated with postoperative uNGAL changes, whereas preoperative serum creatinine levels and the onset of AKI correlated with eGFR at 6 months postoperatively.
Conclusions: uNGAL levels may increase following PN. However, it does not appear to be a useful marker for quantifying the degree of AKI or predicting postoperative renal function in patients with normal contralateral kidney and relatively good preoperative renal function. Further analysis is necessary to assess the usefulness of uNGAL in patients with poor preoperative renal function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Weight CJ, Lythgoe C, Unnikrishnan R, Lane BR, Campbell SC, Fergany AF. Partial nephrectomy does not compromise survival in patients with pathologic upstaging to pT2/pT3 or high-grade renal tumors compared with radical nephrectomy. Urology. 2011; 77: 1142–1146. 10.1016/j.urology.2010.11.058 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weight CJ, Larson BT, Fergany AF, Gao T, Lane BR, Campbell SC, et al. Nephrectomy induced chronic renal insufficiency is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular death and death from any cause in patients with localized cT1b renal masses. J Urol. 2010; 183: 1317–1323. 10.1016/j.juro.2009.12.030 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous