Exposure to p,p'-DDE enhances differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes in a model of sub-optimal differentiation
- PMID: 26200599
- PMCID: PMC6784543
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.07.009
Exposure to p,p'-DDE enhances differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes in a model of sub-optimal differentiation
Abstract
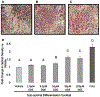
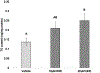
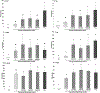
The incidence of obesity is increasing worldwide at an alarming rate. Recently, exposure to environmental contaminants, especially organochlorines such as p,p'-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE), has been implicated as a possible causative factor in the increasing obesity epidemic. The objective of this study was to evaluate the ability of DDE to alter adipogenesis in a model of sub-optimal differentiation. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were induced to differentiate in the presence of DDE (0.01-100μM) using a sub-optimal differentiation cocktail. Eight days after the initiation of differentiation, adipogenesis was assessed through neutral lipid staining, triglyceride accumulation, and expression of markers of terminal differentiation. Exposure to DDE induced a concentration dependent increase in intracellular neutral lipid accumulation as determined by Oil Red O staining and triglyceride assay. Alterations in lipid accumulation were accompanied by upregulation of genetic markers of differentiation. DDE (10μM) enhanced expression of fatty acid binding protein 4 and Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c at the 2.5 and 20μM concentrations. DDE (2.5, 10, and 20μM) induced upregulation of leptin and fatty acid synthase, as compared to sub-optimal vehicle control (0.05% ethanol). Our results indicate that DDE is capable of enhancing adipogenesis and intracellular lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells through upregulation of molecular targets responsible for lipid storage.
Keywords: 3T3-L1; Adipogenesis; Organochlorine insecticides; p,p′-DDE.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vanadium(IV)-chlorodipicolinate inhibits 3T3-L1 preadipocyte adipogenesis by activating LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway.J Inorg Biochem. 2016 Sep;162:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 5. J Inorg Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27318173
-
Suppression of adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation by stearidonic acid (SDA) in 3T3-L1 cells.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Sep 25;16(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0574-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28946872 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC inhibitor Trichostatin A suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 7;13(13):17489-17498. doi: 10.18632/aging.203238. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34232916 Free PMC article.
-
4,4'-Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and 4,4'-dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) promote adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocyte cell culture.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2016 Jul;131:40-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2016.01.005. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27265825
-
Ethanol extracts of Aster yomena (Kitam.) Honda inhibit adipogenesis through the activation of the AMPK signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.Drug Discov Ther. 2017 Nov 22;11(5):281-287. doi: 10.5582/ddt.2017.01046. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Drug Discov Ther. 2017. PMID: 29021504
Cited by
-
Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and obesity.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 May;199:115015. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115015. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35395240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of an environmentally relevant mixture of organochlorine pesticide compounds on adipogenesis and adipocyte function in an immortalized human adipocyte model.Toxicol In Vitro. 2024 Jun;98:105831. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2024.105831. Epub 2024 Apr 20. Toxicol In Vitro. 2024. PMID: 38648980 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 (MCT1) Promotes 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Proliferation and Enhances Insulin Sensitivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 8;23(3):1901. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031901. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163825 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational effects of obesogens.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Aug;125 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):44-57. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13214. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30801972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity and endocrine-disrupting chemicals.Endocr Connect. 2021 Feb;10(2):R87-R105. doi: 10.1530/EC-20-0578. Endocr Connect. 2021. PMID: 33449914 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

