Rap2B promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer through calcium-related ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 26201295
- PMCID: PMC4512009
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12363
Rap2B promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of human breast cancer through calcium-related ERK1/2 signaling pathway
Abstract
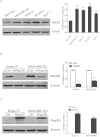
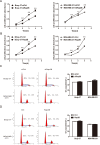
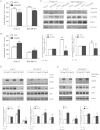
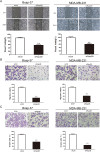
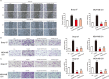
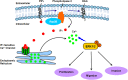
Rap2B, a member of GTP-binding proteins, is widely upregulated in many types of tumors and promotes migration and invasion of human suprarenal epithelioma. However, the function of Rap2B in breast cancer is unknown. Expression of Rap2B was examined in breast cancer cell lines and human normal breast cell line using Western blot analysis. Using the CCK-8 cell proliferation assay, cell cycle analysis, and transwell migration assay, we also elucidated the role of Rap2B in breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Results showed that the expression of Rap2B is higher in tumor cells than in normal cells. Flow cytometry and Western blot analysis revealed that Rap2B elevates the intracellular calcium level and further promotes extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) 1/2 phosphorylation. By contrast, calcium chelator BAPTM/AM and MEK inhibitor (U0126) can reverse Rap2B-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Furthermore, Rap2B knockdown inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities via calcium related-ERK1/2 signaling. In addition, overexpression of Rap2B promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion abilities, which could be neutralized by BAPTM/AM and U0126. Taken together, these findings shed light on Rap2B as a therapeutic target for breast cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rap2B promotes cell adhesion, proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioma.J Neurooncol. 2019 Jun;143(2):221-229. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03163-6. Epub 2019 Apr 17. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 30997639
-
Rap2B promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in prostate cancer.Med Oncol. 2016 Jun;33(6):58. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0771-7. Epub 2016 May 6. Med Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27154636
-
Rap2b promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2016 Oct;36(5):459-64. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2015.1122044. Epub 2015 Dec 16. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2016. PMID: 26671640
-
Rap2B GTPase: structure, functions, and regulation.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7085-93. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5033-y. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27012552 Review.
-
Calcium signalling and breast cancer.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct;94:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30439562 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes of Mutations and Copy-Number and Enhanced Cell Migration during Breast Tumorigenesis.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023 Feb;7(2):e2200072. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200072. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36449747 Free PMC article.
-
Rap2B promotes cell adhesion, proliferation, migration and invasion of human glioma.J Neurooncol. 2019 Jun;143(2):221-229. doi: 10.1007/s11060-019-03163-6. Epub 2019 Apr 17. J Neurooncol. 2019. PMID: 30997639
-
Tumour suppressive function of HUWE1 in thyroid cancer.J Biosci. 2016 Sep;41(3):395-405. doi: 10.1007/s12038-016-9623-z. J Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27581931
-
Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Fundamental Regulatory Differences in Oncogenic HRAS and Isocitrate Dehydrogenase (IDH1) Driven Astrocytoma.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017 Jan;16(1):39-56. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M116.063883. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27834733 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing of malignancy of breast cancer cells after cryopreservation: molecular detection and activation of angiogenesis after CAM-xenotransplantation.BMC Cancer. 2020 Aug 12;20(1):753. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07227-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32787800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J. et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int. J. Cancer. 127, 2893–2917 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz M., Christofori G. & Lehembre F. Distinct mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis. Trends Mol. Med. 13, 535–541 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Torti M. & Lapetina E. G. Structure and function of rap proteins in human platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 71, 533–543 (1994). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

