New and emerging biologic therapies for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: mechanistic rationales and recent clinical data for IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors
- PMID: 26201310
- PMCID: PMC4657465
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.12251
New and emerging biologic therapies for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: mechanistic rationales and recent clinical data for IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors
Abstract
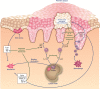
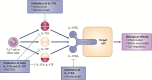
The development of effective and well-tolerated biologic therapies has advanced the management of psoriasis by enabling clinicians to treat underlying disease mechanisms. Biologics approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis include three tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors and an interleukin-12/interleukin-23 inhibitor. The establishment of the immunological basis of psoriasis has led to the development of biologic agents targeting specific downstream mediators in the psoriatic cascade. These drugs inhibit cytokines and cytokine signaling/transcription mediators like interleukin-17, which plays an important role in immunopathogenesis. Several interleukin-17 inhibitors are undergoing phase 3 clinical studies. In addition, biologics that selectively inhibit interleukin-23 have been assessed in phase 2 studies. This review describes how the dissection of pathways in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis has led to the development of therapeutic agents and highlights the latest clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability data on new and emerging biologic therapies that selectively target interleukin-17 or interleukin-23.
Keywords: biologic; interleukin-17; interleukin-23; psoriasis.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of IL-17 in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Update on IL-17 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Plaque Psoriasis.J Cutan Med Surg. 2016 Nov;20(6):509-516. doi: 10.1177/1203475416651605. Epub 2016 May 20. J Cutan Med Surg. 2016. PMID: 27207350 Review.
-
New biologics in psoriasis: an update on IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors.Cutis. 2017 Feb;99(2):123-127. Cutis. 2017. PMID: 28319618 Review.
-
Biologic therapies targeting the interleukin (IL)-23/IL-17 immune axis for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Jan;34(1):30-38. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15879. Epub 2019 Sep 4. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020. PMID: 31419343
-
Unveiling the effectiveness and safety spectrum of biologic therapies in psoriasis: a three-year real-world analysis.Postgrad Med. 2025 Apr-May;137(3-4):299-308. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2025.2493042. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Postgrad Med. 2025. PMID: 40227059
-
IL-17 inhibitors for psoriasis.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018 Sep;37(3):148-157. doi: 10.12788/j.sder.2018.051. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2018. PMID: 30215631 Review.
Cited by
-
Erythema Dyschromicum Perstans After Adalimumab Treatment.Cureus. 2022 Dec 6;14(12):e32264. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32264. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36620779 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of the inverse retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γ agonist AZD0284.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;86(7):1398-1405. doi: 10.1111/bcp.14253. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32067249 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Role of IL-17 in plaque psoriasis: therapeutic potential of ixekizumab.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017 Mar 13;13:315-323. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S111107. eCollection 2017. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017. PMID: 28352182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the relative efficacy of interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 targeted treatments for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of PASI response.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 14;14(8):e0220868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220868. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31412060 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Dec;55(3):379-390. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8702-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30109481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nast A, Boehncke WH, Mrowietz U, et al. S3—Guidelines on the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris (English version). Update. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10(Suppl 2):S1–S95. - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. 2012. Psoriasis: The assessment and management of psoriasis. NICE clinical guideline 153. Available at: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg153/resources/guidance-psoriasis-pdf. Accessed February 13, 2015.
-
- Pathirana D, Ormerod AD, Saiag P, et al. European S3-guidelines on the systemic treatment of psoriasis vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2009;23(Suppl 2):1–70. - PubMed
-
- Puig L, Carrascosa JM, Daudén E, et al. [Spanish evidence-based guidelines on the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis with biologic agents] Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2009;100:386–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

