Randomised clinical trial: a dose-ranging study of vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. lansoprazole for the treatment of erosive oesophagitis
- PMID: 26201312
- PMCID: PMC5014135
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.13331
Randomised clinical trial: a dose-ranging study of vonoprazan, a novel potassium-competitive acid blocker, vs. lansoprazole for the treatment of erosive oesophagitis
Abstract
Background: The potassium-competitive acid blocker vonoprazan (VPZ) has potent acid-inhibitory effects and may offer clinical advantages over conventional therapy for acid-related disorders.
Aim: To investigate the efficacy and safety of VPZ in patients with erosive oesophagitis (EO).
Methods: In this multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, dose-ranging study, patients ≥20 years with endoscopically confirmed EO [Los Angeles (LA) grades A-D] received VPZ 5, 10, 20 or 40 mg, or lansoprazole (LPZ) 30 mg once daily for 8 weeks. The primary endpoint was the proportion of healed EO subjects as shown by endoscopy at week 4.
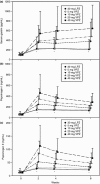
Results: A total of 732 subjects received VPZ or LPZ. The proportion of healed EO subjects at week 4 was 92.3%, 92.5%, 94.4%, 97.0% and 93.2%, respectively, with VPZ 5, 10, 20 and 40 mg and LPZ 30 mg. All VPZ doses were non-inferior to LPZ when adjusted for baseline LA grades A/B and C/D. Among those with LA grades C/D, the proportions of healed EO subjects were 87.3%, 86.4%, 100%, 96.0% and 87.0%, respectively, with VPZ 5, 10, 20 and 40 mg and LPZ 30 mg. The incidence of adverse events was similar across the groups.
Conclusions: Vonoprazan was effective and non-inferior to LPZ in healing EO. VPZ 20 mg or higher was highly efficacious for severe EO (LA grades C/D). VPZ was associated with no safety concern during this 8-week study, while there was a dose-dependent increase in serum gastrin. Once-daily VPZ 20 mg is the recommended clinical dose for treating EO.
© 2015 The Authors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Chiba N, De Gara CJ, Wilkinson JM, et al Speed of healing and symptom relief in grade II to IV gastroesophageal reflux disease: a meta‐analysis. Gastroenterology 1997; 112: 1798–810. - PubMed
-
- Edwards SJ, Lind T, Lundell L, et al Systematic review: standard‐ and double‐dose proton pump inhibitors for the healing of severe erosive oesophagitis – a mixed treatment comparison of randomized controlled trials. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009; 30: 547–56. - PubMed
-
- Fennerty MB, Johanson JF, Hwang C, et al Efficacy of esomeprazole 40 mg vs. lansoprazole 30 mg for healing moderate to severe erosive oesophagitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 21: 455–63. - PubMed
-
- Vakil NB, Shaker R, Johnson DA, et al The new proton pump inhibitor esomeprazole is effective as a maintenance therapy in GERD patients with healed erosive oesophagitis: a 6‐month, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of efficacy and safety. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2001; 15: 927–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources