HiSCR (Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response): a novel clinical endpoint to evaluate therapeutic outcomes in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa from the placebo-controlled portion of a phase 2 adalimumab study
- PMID: 26201313
- PMCID: PMC5034809
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.13216
HiSCR (Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response): a novel clinical endpoint to evaluate therapeutic outcomes in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa from the placebo-controlled portion of a phase 2 adalimumab study
Abstract
Background: Determining treatment response for patients with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) can be challenging due to limitations of current disease activity evaluations.
Objective: Evaluate the novel, validated endpoint, Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) and its utility as an outcome measure.
Methods: Patients with baseline total abscess and inflammatory nodule count (AN count) of at least three and draining fistula count of 20 or fewer comprised the post hoc subpopulation analysed. HiSCR (at least a 50% reduction in total AN count, with no increase in abscess count, and no increase in draining fistula count relative to baseline) and HS-PGA Response [Hidradenitis Suppurativa-Physician's Global Assessment score of clear, minimal, or mild, with at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline] were used to evaluate patient response after adalimumab treatment weekly, every other week, or placebo (1 : 1 : 1).
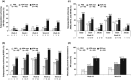
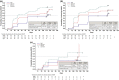
Results: The subpopulation included 132 (85.7%) patients; 70.5% women and 73.5% white. At week 16, HiSCR was achieved by 54.5% receiving weekly adalimumab, 33.3% every other week, and 25.6% placebo and HS-PGA Response was achieved by 20.5% receiving weekly adalimumab, 6.7% every other week and 2.3% placebo.
Conclusion: HiSCR was more responsive to change than HS-PGA Response in this subpopulation.
© 2015 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures
References
-
- Menter A, Tyring SK, Gordon K et al Adalimumab therapy for moderate to severe psoriasis: a randomized, controlled phase III trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 2008; 58: 106–115. - PubMed
-
- Nazary M, van der Zee HH, Prens EP et al Pathogenesis and pharmacotherapy of Hidradenitis suppurativa. Eur J Pharmacol 2011; 672: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Adams DR, Gordon KB, Devenyi AG, Ioffreda MD. Severe hidradenitis suppurativa treated with infliximab infusion. Arch Dermatol 2003; 139: 1540–1542. - PubMed
-
- Hurley HJ. Hidradenitis Suppurativa In Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH, Jr, eds. Dermatologic Surgery: Principles and Practice, 2nd edn Marcel Dekker, New York, 1996: 623–645.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

