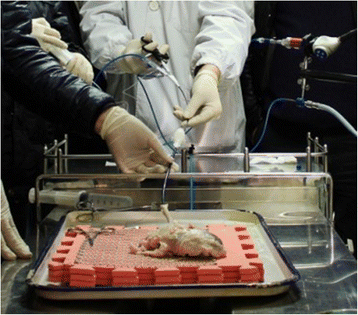
Flexible ureteroscopy training for surgeons using isolated porcine kidneys in vitro
- PMID: 26201465
- PMCID: PMC4512109
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-015-0067-9
Flexible ureteroscopy training for surgeons using isolated porcine kidneys in vitro
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the feasibility of flexible ureteroscopy training by using isolated porcine kidneys and ureters in vitro.
Methods: Twenty young urologists were randomly divided into four groups. Overall performance was assessed based on a global rating scale, pass/fail rating, total time to complete task, learning curve, incidence of trauma, and perforations. The effect of training was determined by comparing their performance in baseline with that in the post-test.
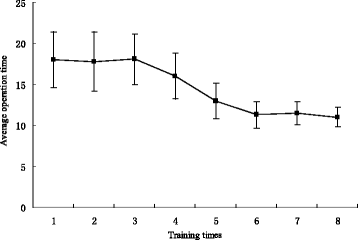
Results: After the training, average operation time significantly decreased from 18 ± 3.4 min to 11 ± 1.2 min (P < 0.05). The urologists exhibited a relatively stable performance level after the sixth operation. Significant differences were observed between pre-test and post-test with respect to the global rating scale and the pass/fail rating (P < 0.05). However, the incidence of mucosal trauma and perforations did not change significantly (P = 0.26 and 0.35, respectively).
Conclusions: The isolated porcine kidneys are convenient and intuitive models for young urologists to practice flexible ureteroscopy on.
Figures
References
-
- Knudsen B, Miyaoka R, Shah K, Holden T, Turk TM, Pedro RN, Kriedberg C, Hinck B, Ortiz-Alvarado O, Monga M. Durability of the next generation flexible flberoptic ureteroscopes: a randomized prospective multi-institutional clinical trial. Urology. 2010;75:534–8. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2009.06.093. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources