Multiple B-cell epitope vaccine induces a Staphylococcus enterotoxin B-specific IgG1 protective response against MRSA infection
- PMID: 26201558
- PMCID: PMC4511869
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12371
Multiple B-cell epitope vaccine induces a Staphylococcus enterotoxin B-specific IgG1 protective response against MRSA infection
Abstract
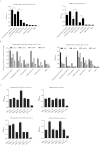
No vaccine against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has been currently approved for use in humans. Staphylococcus enterotoxin B (SEB) is one of the most potent MRSA exotoxins. In the present study, we evaluated the efficacy and immunologic mechanisms of an SEB multiple B-cell epitope vaccine against MRSA infection. Synthetic overlapping peptide ELISA identified three novel B-cell immunodominant SEB epitopes (in addition to those previously known): SEB31-48, SEB133-150, and SEB193-210. Six B-cell immunodominant epitopes (amino acid residues 31-48, 97-114, 133-150, 193-210, 205-222, and 247-261) were sufficient to induce robust IgG1/IgG2b-specific protective responses against MRSA infection. Therefore, we constructed a recombinant MRSA SEB-specific multiple B-cell epitope vaccine Polypeptides by combining the six SEB immunodominant epitopes and demonstrated its ability to induce a robust SEB-specific IgG1 response to MRSA, as well as a Th2-directing isotype response. Moreover, Polypeptides-induced antisera stimulated synergetic opsonophagocytosis killing of MRSA. Most importantly, Polypeptides was more effective at clearing the bacteria in MRSA-infected mice than the whole SEB antigen, and was able to successfully protect mice from infection by various clinical MRSA isolates. Altogether, these results support further evaluation of the SEB multiple B-cell epitope-vaccine to address MRSA infection in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fine-mapping of immunodominant linear B-cell epitopes of the Staphylococcus aureus SEB antigen using short overlapping peptides.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 5;9(3):e90445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090445. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24599257 Free PMC article.
-
Immunisation With Immunodominant Linear B Cell Epitopes Vaccine of Manganese Transport Protein C Confers Protection against Staphylococcus aureus Infection.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0149638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149638. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26895191 Free PMC article.
-
c-di-GMP as a vaccine adjuvant enhances protection against systemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection.Vaccine. 2009 Jul 30;27(35):4867-73. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.04.053. Epub 2009 May 9. Vaccine. 2009. PMID: 19406185
-
Humanized staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB)-specific monoclonal antibodies protect from SEB intoxication and Staphylococcus aureus infections alone or as adjunctive therapy with vancomycin.J Infect Dis. 2014 Sep 15;210(6):973-81. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu198. Epub 2014 May 5. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24803533 Free PMC article.
-
A highly neutralizing human monoclonal antibody targeting a novel linear epitope on staphylococcal enterotoxin B.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2360338. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2360338. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 38857905 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Epitope-Based Vaccines: The Next Generation of Promising Vaccines Against Bacterial Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;13(3):248. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030248. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping of B-cell epitopes on the N- terminal and C-terminal segment of nucleocapsid protein from Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 20;13(9):e0204264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204264. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30235312 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Suppresses Th2-Induced by Trichinella spiralis Infection and Downregulates Serine Protease Genes Expression: A Critical Role in Vaccine Development.Iran J Parasitol. 2023 Apr-Jun;18(2):172-181. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v18i2.13183. Iran J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37583627 Free PMC article.
-
New Is Old, and Old Is New: Recent Advances in Antibiotic-Based, Antibiotic-Free and Ethnomedical Treatments against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Wound Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 25;17(5):617. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050617. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27120596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunization with recombinant fusion of LTB and linear epitope (40-62) of epsilon toxin elicits protective immune response against the epsilon toxin of Clostridium perfringens type D.AMB Express. 2019 Jul 12;9(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0824-3. AMB Express. 2019. PMID: 31300915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakamura A. et al.. Association between antimicrobial consumption and clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a 14-year study. J Infect Chemother. 18, 90–95 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zhu D. et al.. China’s CHINET surveillance of bacterial resistance In 2010. Chinese Journal of infection and chemotherapy. 5, 326–329 (2011).
-
- Nakamura A. et al.. Association between antimicrobial consumption and clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a 14-year study. J Infect Chemother. 18, 90–95 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

