Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of incobotulinumtoxina for upper-limb post-stroke spasticity
- PMID: 26201835
- PMCID: PMC5064747
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.24776
Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of incobotulinumtoxina for upper-limb post-stroke spasticity
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Muscle Nerve. 2016 Jun;54(1):170. doi: 10.1002/mus.25182. Muscle Nerve. 2016. PMID: 27297960 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Efficacy and safety of incobotulinumtoxinA in post-stroke upper-limb spasticity were studied.
Methods: Subjects randomized 2:1 to incobotulinumtoxinA (fixed dose 400 U) or placebo, with fixed doses for the primary target clinical pattern (PTCP; flexed elbow, 200 U; flexed wrist, 150 U; clenched fist, 100 U). Doses for non-primary patterns were flexible within predefined ranges.
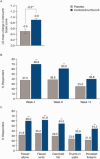
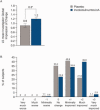
Results: At week 4, incobotulinumtoxinA led to larger improvements in PTCP Ashworth scale (AS) scores than placebo [least-squares mean change ± standard error: -0.9 ± 0.06 (n = 171) vs. -0.5 ± 0.08 (n = 88); P < 0.001], and more subjects were PTCP AS responders (≥1-point improvement) with incobotulinumtoxinA (69.6%) than with placebo (37.5%; P < 0.001). Investigator's Global Impression of Change confirmed superiority of incobotulinumtoxinA vs. placebo (P = 0.003). IncobotulinumtoxinA was associated with functional improvements, as demonstrated in responder rates for Disability Assessment Scale principal target at week 4 (P = 0.007). Adverse events were mainly mild/moderate, and were reported by 22.4% (incobotulinumtoxinA) and 16.8% (placebo) of subjects.
Conclusions: IncobotulinumtoxinA significantly improved upper-limb spasticity and associated disability, and was well-tolerated.
Keywords: Xeomin; botulinum toxins, type A; incobotulinumtoxinA; muscle spasticity; stroke.
© 2015 The Authors. Muscle and Nerve published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Kanovský P, Slawek J, Denes Z, Platz T, Sassin I, Comes G, et al Efficacy and safety of botulinum neurotoxin NT 201 in poststroke upper‐limb spasticity. Clin Neuropharmacol 2009;32:259–265. - PubMed
-
- Bakheit AM, Thilmann AF, Ward AB, Poewe W, Wissel J, Muller J, et al A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐ranging study to compare the efficacy and safety of three doses of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) with placebo in upper‐limb spasticity after stroke. Stroke 2000;31:2402–2406. - PubMed
-
- Brashear A, Gordon MF, Elovic E, Kassicieh VD, Marciniak C, Do M, et al Intramuscular injection of botulinum toxin for the treatment of wrist and finger spasticity after a stroke. N Engl J Med 2002;347:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Simpson DM, Alexander DN, O'Brien CF, Tagliati M, Aswad AS, Leon JM, et al Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of upper extremity spasticity: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology 1996;46:1306–1310. - PubMed
-
- Simpson DM, Gracies JM, Yablon SA, Barbano R, Brashear A, BoNT/TZD Study Team . Botulinum neurotoxin versus tizanidine in upper‐limb spasticity: a placebo‐controlled study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009;80:380–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

