Linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery in 140 brain metastases from malignant melanoma
- PMID: 26201853
- PMCID: PMC4511446
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1517-1
Linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery in 140 brain metastases from malignant melanoma
Abstract
Background: To retrospectively access outcome and prognostic parameters of linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery in brain metastases from malignant melanoma.
Methods: Between 1990 and 2011 140 brain metastases in 84 patients with malignant melanoma (median age 56 years) were treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. At initial stereotactic radiosurgery 48 % of patients showed extracerebral control. The median count of brain metastases in a single patient was 1, the median diameter was 12 mm. The median dose applied was 20 Gy/80 % isodose enclosing.
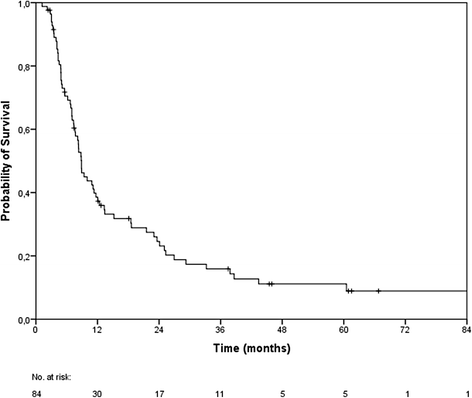
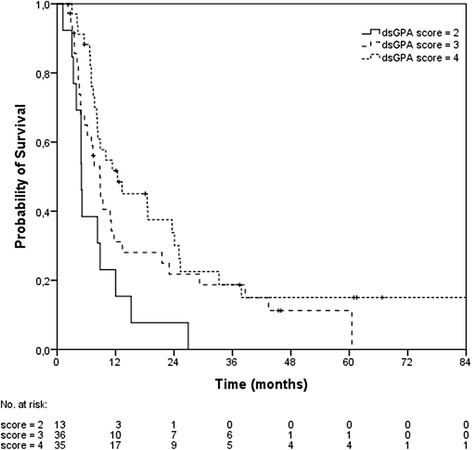
Results: The median follow-up was 7 months and the median overall survival 9 months. The 6-, 12- and 24 month overall survival rates were 71 %, 39 % and 25 % respectively. Cerebral follow-up imaging showed complete remission in 20 brain metastases, partial remission in 39 brain metastases, stable disease in 54 brain metastases, progressive disease in 24 brain metastases and pseudo-progression in 3 brain metastases. Median intracerebral control was 5.3 months and the 6- and 12-month intracerebral progression-free survival rates 48 % and 38 %, respectively. Upon univariate analysis, extracerebral control (log-rank, p < 0.001), the response to stereotactic radiosurgery (log-rank, p < 0.001), the number of brain metastases (log-rank, p = 0.007), the recursive partitioning analysis class (log-rank, p = 0.027) and the diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment score (log-rank, p = 0.011) were prognostic for overall survival. The most common clinical side effect was headache common toxicity criteria grade I. The most common radiological finding during follow-up was localized edema within the stereotactic radiosurgery high dose region.
Conclusion: Stereotactic radiosurgery is a well-tolerated and effective treatment option for brain metastases in malignant melanoma and was able to achieve local remissions in several cases. Furthermore, especially patients with controlled extracerebral disease and a low count of brain metastases seem to benefit from this treatment modality. Prospective trials analysing the effects of combined stereotactic radiosurgery and new systemic agents are warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential role for LINAC-based stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of 5 or more radioresistant melanoma brain metastases.J Neurosurg. 2015 Nov;123(5):1261-7. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.JNS141919. Epub 2015 Jul 3. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 26140482
-
Impact of 2-staged stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases ≥ 2 cm.J Neurosurg. 2018 Aug;129(2):366-382. doi: 10.3171/2017.3.JNS162532. Epub 2017 Sep 22. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28937324
-
Radiosurgery in the management of brain metastasis: a retrospective single-center study comparing Gamma Knife and LINAC treatment.J Neurosurg. 2018 Feb;128(2):352-361. doi: 10.3171/2016.10.JNS161480. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28338441
-
Overall survival following stereotactic radiosurgery for ten or more brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 19;23(1):1004. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11452-7. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37858075 Free PMC article.
-
Linear Accelerator-Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cranial Intraparenchymal Metastasis of a Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor: Case Report and Review of the Literature.World Neurosurg. 2019 Mar;123:123-127. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.11.231. Epub 2018 Dec 7. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 30529515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of machine learning model to predict early death of melanoma brain metastasis patients.Front Oncol. 2025 Jul 8;15:1517961. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1517961. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40697382 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic melanoma: prognostic factors and survival in patients with brain metastases.J Neurooncol. 2017 Dec;135(3):507-512. doi: 10.1007/s11060-017-2591-9. Epub 2017 Aug 17. J Neurooncol. 2017. PMID: 28819707 Free PMC article.
-
Frameless stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Aug 13;47(1):423. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02666-9. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39136823
-
Frameless Stereotactic Radiosurgery With Linear Accelerator (LINAC)-Based Technology for Brain Metastases: Outcomes Analysis in 141 Patients.Cureus. 2021 Jun 6;13(6):e15475. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15475. eCollection 2021 Jun. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34262813 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of a nomogram for melanomas with brain metastases at initial diagnosis.Cancer Med. 2019 Dec;8(18):7577-7585. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2644. Epub 2019 Oct 27. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31657530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krebs in Deutschland 2007/2008. 8. Ausgabe. Robert Koch-Institut (Hrsg) und die Gesellschaft der epidemiologischen Krebsregister inDeutschland e.V. (Hrsg). Berlin, 2012.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical