Early markers of right heart involvement in regular smokers by Pocket Size Imaging Device
- PMID: 26201963
- PMCID: PMC4511232
- DOI: 10.1186/s12947-015-0024-5
Early markers of right heart involvement in regular smokers by Pocket Size Imaging Device
Abstract
Purpose: To test the diagnostic power of Pocket Size Imaging Device (PSID) in detecting early signs of right heart (RH) involvement in regular smokers (RS) free of overt cardiac involvement.
Methods: One-hundred-forty-three regular smokers and 51 healthy controls, comparable for age and sex, underwent physical exam (PE), PSID exam and standard echocardiography. Based on a simplified Boston score, ≥1 of clinical signs (jugular venous distension, hepatomegaly, peripheral pitting oedema and abnormal pulmonary sounds) were considered indicative of RH involvement. A composite score (1 to 4) obtained by summing the points of four quantitative RH abnormalities detectable by PSID (inferior vena cava [IVC] dilatation, reduced IVC respiratory variation, right ventricular dilatation and right atrial dilatation), was generated and ≥1 of PSID abnormal signs was considered indicative of RH involvement.
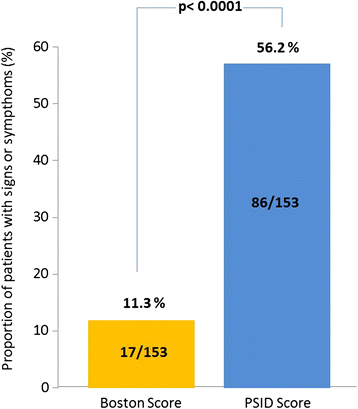
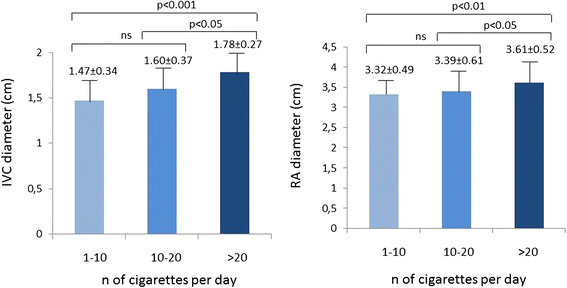
Results: Boston score was not significantly different between the two groups. By using PSID, smokers exhibited greater IVC diameter (p < 0.0001), right atrial diameter (p < 0.002) and higher PSID score (p < 0.005) than controls. Compared to PE, the additional diagnostic power of PSID (≥1 abnormal sign of both Boston and PSID score) was 44.9% in smokers. By dividing smokers in tertiles according to number of cigarettes per day, the third tertile showed the largest values of both IVC and right atrial dimension. Differences were confirmed by standard echocardiography. Reproducibility of PSID measurements and concordance of linear measurements between PSID and standard echo measurements was very good except for concordance of right ventricular basal diameter.
Conclusions: PSID detects early ultrasound signs of RH involvement in regular otherwise healthy smokers in comparison with PE.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the main determinants of abdominal aorta size: a screening by Pocket Size Imaging Device.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017 Jan 13;15(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12947-016-0094-z. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017. PMID: 28086907 Free PMC article.
-
Pocket-size imaging device: effectiveness for ward-based transthoracic studies.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Dec;14(12):1132-9. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jet091. Epub 2013 May 24. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23708845
-
Bedside screening with the use of pocket-size imaging device can be useful for ruling out carotid artery stenosis in patients scheduled for cardiac surgery.Echocardiography. 2017 May;34(5):716-722. doi: 10.1111/echo.13507. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Echocardiography. 2017. PMID: 28299809 Clinical Trial.
-
Assessment of right ventricular systolic function by tissue Doppler echocardiography.Dan Med J. 2012 Mar;59(3):B4409. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22381093 Review.
-
The role of echocardiography in suspected and established PE.Semin Vasc Med. 2001 Nov;1(2):165-74. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-18484. Semin Vasc Med. 2001. PMID: 15199499 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the main determinants of abdominal aorta size: a screening by Pocket Size Imaging Device.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017 Jan 13;15(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12947-016-0094-z. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2017. PMID: 28086907 Free PMC article.
-
Results of ACCORDIAN in ACCORD with lower blood pressure begetting lower mortality in patients with diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Jun;20(6):1335-1336. doi: 10.1111/dom.13249. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29424470 Free PMC article.
-
Focused cardiac ultrasound as a predictor of readmission in acute decompensated heart failure.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Jul;34(7):1075-1079. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-1317-1. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29450742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for disease control and prevention Cigarette smoking among adults – United States 2007. MMWR. 2008;57:1221–1226. - PubMed
-
- CDC Smoking-attributable mortality, years and potential life lost, and productivity losses – United States, 2000–2004. MMWR. 2008;45:1226–1228. - PubMed
-
- European Commission. Attitudes of Europeans Towards Tobacco. Special Eurobarometer 385 / Wave EB77.1 – TNS Opinion & Social (May 2012). http://ec.europa.eu/public_opinion/index_en.htm.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

