New "haploid biofilm model" unravels IRA2 as a novel regulator of Candida albicans biofilm formation
- PMID: 26202015
- PMCID: PMC5378891
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12433
New "haploid biofilm model" unravels IRA2 as a novel regulator of Candida albicans biofilm formation
Abstract
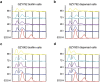
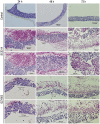
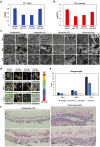
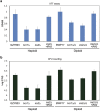
Clinical isolates of the fungal human pathogen Candida albicans are invariably diploid and heterozygous, impeding genetic study. Recent isolation of C. albicans haploids opens opportunities to apply technologies unfeasible in diploids. However, doubts remain on whether the haploids, derived from chromosome loss, can represent the diploids. Here, we use C. albicans haploids to investigate biofilm, a key virulence attribute. We conducted the first comprehensive characterization of biofilm formation of the haploids in comparison with the diploids. We demonstrate that the haploids form biofilms with essentially the same characteristics as the diploids. Screening a haploid mutant library has uncovered novel GTPase-related genes as biofilm regulators, including IRA2 that encodes an activator of the Ras GTPase. IRA2-deletion mutants develop poorly constructed biofilm in both haploid and diploid C. albicans. Our results demonstrate that the haploids are a valid model for C. albicans biofilm research and a powerful tool for uncovering novel regulators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sdd3 regulates the biofilm formation of Candida albicans via the Rho1-PKC-MAPK pathway.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0328324. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03283-24. Epub 2024 Dec 17. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39688394 Free PMC article.
-
The 'obligate diploid' Candida albicans forms mating-competent haploids.Nature. 2013 Feb 7;494(7435):55-9. doi: 10.1038/nature11865. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Nature. 2013. PMID: 23364695 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Candida albicans hyphal wall protein 1 (HWP1) genotype on biofilm production and fungal susceptibility to microglial cells.Microb Pathog. 2014 Apr-May;69-70:20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2014.03.003. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Microb Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24685698
-
The parasexual lifestyle of Candida albicans.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Dec;28:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.06.017. Epub 2015 Jul 25. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26210747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candida albicans biofilms: more than filamentation.Curr Biol. 2005 Jun 21;15(12):R453-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.020. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15964263 Review.
Cited by
-
Lrg1 Regulates β (1,3)-Glucan Masking in Candida albicans through the Cek1 MAP Kinase Pathway.mBio. 2019 Sep 17;10(5):e01767-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01767-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31530671 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial GtfB Augments Candida albicans Accumulation in Cross-Kingdom Biofilms.J Dent Res. 2017 Sep;96(10):1129-1135. doi: 10.1177/0022034517714414. Epub 2017 Jun 12. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 28605597 Free PMC article.
-
Sdd3 regulates the biofilm formation of Candida albicans via the Rho1-PKC-MAPK pathway.mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0328324. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03283-24. Epub 2024 Dec 17. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39688394 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivating the mannose-ethanolamine phosphotransferase Gpi7 confers caspofungin resistance in the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans.Cell Surf. 2021 Jun 23;7:100057. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2021.100057. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cell Surf. 2021. PMID: 34258484 Free PMC article.
-
Sac7 and Rho1 regulate the white-to-opaque switching in Candida albicans.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 17;8(1):875. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19246-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29343748 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashman R. B., Farah C. S., Wanasaengsakul S., Hu Y., Pang G. & Clancy R. L. Innate versus adaptive immunity in Candida albicans infection. Immunology and cell biology 82, 196–204 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Seneviratne C. J., Jin L. & Samaranayake L. P. Biofilm lifestyle of Candida: a mini review. Oral diseases 14, 582–590 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

