Patient experiences in retinal trials: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 26202164
- PMCID: PMC4511246
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-015-0071-6
Patient experiences in retinal trials: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Patient-centered care recognizes the obligation to understand and meet patient's expectations. An individual's satisfaction has been found to affect health-related decisions and treatment-related behaviours, which in turn affect medical compliance, follow-up, the success of treatment and the appropriate use of services. We studied the expectations, experiences and satisfaction of patients who participated in clinical trials for retinal diseases at the Sydney Eye Hospital.
Methods: The study was undertaken at the research clinic of the major public quaternary eye hospital in New South Wales, Australia. A 37-question survey was conducted on patients enrolled in or who had finished a clinical trial for macular disease in the 12 months preceding this study in November 2012. Patient satisfaction was assessed using close-ended, multiple choice questions. First, the decision making process for entering into the clinical trial was evaluated. Then the level of patient understanding and experience during the study was assessed. Finally, there was a series of questions to gauge the participants' perception of trial outcomes and overall impression gained from the experience.
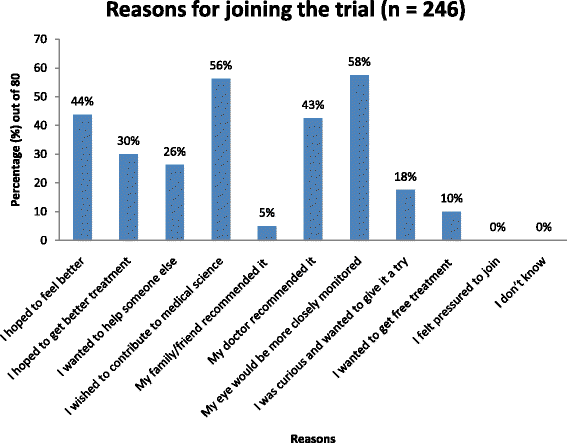
Results: Eighty patients completed the questionnaire. Overall patient satisfaction was high with the majority of patients stating they would recommend participation in a retinal clinical trial (94 %) and participate in a subsequent trial (78 %). Most patients rated themselves as the most important factor in making the decision to join a trial. Patients felt well informed and expectations were generally felt to be met, however 14 % did not believe that they could withdraw from the study voluntarily. The most common reasons for trial participation were to contribute to medical science and to have improved treatment outcomes.
Conclusions: We found that patients generally found participation in retinal clinical trials to be a positive experience. Factors contributing to dissatisfaction mainly related to inconvenience experienced by transportation and waiting times. We also found that patients felt well informed about the study, but some did not have a complete understanding of their rights, which had been communicated to them when they entered the study. There were both altruistic and self-motivated reasons behind patients' decisions to join a retinal trial.
Figures
References
-
- Turnbull JE, Luther KM. Patient satisfaction report paves way to improved care. QRC Advisor. 1996;13(1):1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous