Downregulation of cancer stem cell properties via mTOR signaling pathway inhibition by rapamycin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PMID: 26202311
- PMCID: PMC4532219
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3100
Downregulation of cancer stem cell properties via mTOR signaling pathway inhibition by rapamycin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Abstract
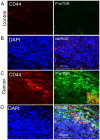
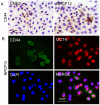
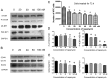
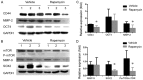
Rapamycin, a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling inhibitor, inhibits cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation, including in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), which we proved in a previous study. However, whether rapamycin affects cancer stem cells (CSCs) is unclear. In examining samples of NPCs, we found regions of CD44-positive cancer cells co-expressing the stem cell biomarker OCT4, suggesting the presence of CSCs. Following this, we used double-label immunohistochemistry to identify whether the mTOR signaling pathway was activated in CD44-positive CSCs in NPCs. We used a CCK-8 assay and western blotting to explore whether the stem cell biomarkers CD44 and SOX2 and the invasion protein MMP-2 could be suppressed by treatment with rapamycin in cultured primary NPC cells and secondary tumors in BALB/c nude mice. Interestingly, we found that rapamycin inhibited mTOR signaling in addition to simultaneously downregulating the expression of CD44, SOX2 and MMP-2 and that it affected cell growth and tumor size and weight both in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, we confirmed for the first time that CSC properties are reduced and invasion potential is restrained in response to mTOR signaling inhibition in NPC. This evidence indicates that the targeted inhibition of CSC properties may provide a novel strategy to treat cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
mTOR activation in immature cells of primary nasopharyngeal carcinoma and anti-tumor effect of rapamycin in vitro and in vivo.Cancer Lett. 2013 Dec 1;341(2):186-94. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.004. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23933173
-
[Activation of mTOR signaling pathway in cancer stem cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and inhibitive effect of rapamycin against the cancer stem cells].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Jul;29(13):1179-84. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26540919 Chinese.
-
XIAP Limits Autophagic Degradation of Sox2 and Is A Therapeutic Target in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Stem Cells.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 5;8(6):1494-1510. doi: 10.7150/thno.21717. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29556337 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between telomerase and mTOR pathway in cancer stem cells.Gene. 2018 Jan 30;641:235-239. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.072. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29074462 Review.
-
The Roles of mTOR Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: From Pathogenesis to Therapy.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024;17:e18761429293675. doi: 10.2174/0118761429293675240709061332. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38988161 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapamycin inhibited the function of lung CSCs via SOX2.Tumour Biol. 2016 Apr;37(4):4929-37. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4341-y. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26526583
-
Dihydroartemisinin Prevents Distant Metastasis of Laryngeal Carcinoma by Inactivating STAT3 in Cancer Stem Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Mar 16;26:e922348. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922348. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32176678 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Activated mTORC1 and mTORC2 Coordinately Promote Nasopharyngeal Cancer Stem Cell Properties.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0194121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01941-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35019715 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Feb 7;5(1):8. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0110-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32296030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UBE2T promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by activating the AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):15161-72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7805. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26943030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feng BJ, Huang W, Shugart YY, Lee MK, Zhang F, Xia JC, Wang HY, Huang TB, Jian SW, Huang P, et al. Genome-wide scan for familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals evidence of linkage to chromosome 4. Nat Genet. 2002;31:395–399. - PubMed
-
- Shueng PW, Shen BJ, Wu LJ, Liao LJ, Hsiao CH, Lin YC, Cheng PW, Lo WC, Jen YM, Hsieh CH. Concurrent image-guided intensity modulated radiotherapy and chemotherapy following neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:95. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-95. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

