Nutritional systems biology of type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 26202330
- PMCID: PMC4512958
- DOI: 10.1007/s12263-015-0481-3
Nutritional systems biology of type 2 diabetes
Abstract
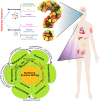
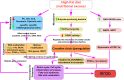
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) has become an increasingly challenging health burden due to its high morbidity, mortality, and heightened prevalence worldwide. Although dietary and nutritional imbalances have long been recognized as key risk factors for T2D, the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The advent of nutritional systems biology, a field that aims to elucidate the interactions between dietary nutrients and endogenous molecular entities in disease-related tissues, offers unique opportunities to unravel the complex mechanisms underlying the health-modifying capacities of nutritional molecules. The recent revolutionary advances in omics technologies have particularly empowered this incipient field. In this review, we discuss the applications of multi-omics approaches toward a systems-level understanding of how dietary patterns and particular nutrients modulate the risk of T2D. We focus on nutritional studies utilizing transcriptomics, epigenomomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and microbiomics, and integration of diverse omics technologies. We also summarize the potential molecular mechanisms through which nutritional imbalances contribute to T2D pathogenesis based on these studies. Finally, we discuss the remaining challenges of nutritional systems biology and how the field can be optimized to further our understanding of T2D and guide disease management via nutritional interventions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Foodomics as part of the host-microbiota-exposome interplay.J Proteomics. 2016 Sep 16;147:3-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.04.033. Epub 2016 Apr 26. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27130534 Review.
-
Sepsis: deriving biological meaning and clinical applications from high-dimensional data.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2021 May 7;9(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40635-021-00383-x. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2021. PMID: 33961170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omics era in type 2 diabetes: From childhood to adulthood.World J Diabetes. 2021 Dec 15;12(12):2027-2035. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.2027. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 35047117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Pharmacomultiomics for Precision Medicine in Diabetes: A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 12;13(2):447. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020447. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002860 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omic data integration and analysis using systems genomics approaches: methods and applications in animal production, health and welfare.Genet Sel Evol. 2016 Apr 29;48(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0217-x. Genet Sel Evol. 2016. PMID: 27130220 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico investigation of molecular networks linking gastrointestinal diseases, malnutrition, and sarcopenia.Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 4;9:989453. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.989453. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36407505 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of genomics and post-genomics research on type 2 diabetes mellitus: Future perspectives and a framework for further studies.J Biosci. 2019 Mar;44(1):21. J Biosci. 2019. PMID: 30837372 Review.
-
Effect of Uncaria tomentosa aqueous extract on the response to palmitate-induced lipotoxicity in cultured skeletal muscle cells.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Nov 15;23(1):412. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04204-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37968654 Free PMC article.
-
Network Modeling Approaches and Applications to Unravelling Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Genes (Basel). 2019 Nov 24;10(12):966. doi: 10.3390/genes10120966. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31771247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction and applications of consensus yeast metabolic network based on RNA sequencing.FEBS Open Bio. 2016 Feb 27;6(4):264-75. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12033. eCollection 2016 Apr. FEBS Open Bio. 2016. PMID: 27239440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmad S, et al. PPAR signaling pathway is a key modulator of liver proteome in pups born to vitamin B-12 deficient rats. J Proteomics. 2013;91:297–308. - PubMed
-
- Alberti KGM, Zimmet P. Epidemiology: global burden of disease—Where does diabetes mellitus fit in? Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9:258–260. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

