Toll pathway modulates TNF-induced JNK-dependent cell death in Drosophila
- PMID: 26202785
- PMCID: PMC4632500
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.140171
Toll pathway modulates TNF-induced JNK-dependent cell death in Drosophila
Abstract
Signalling networks that control the life or death of a cell are of central interest in modern biology. While the defined roles of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway in regulating cell death have been well-established, additional factors that modulate JNK-mediated cell death have yet to be fully elucidated. To identify novel regulators of JNK-dependent cell death, we performed a dominant-modifier screen in Drosophila and found that the Toll pathway participates in JNK-mediated cell death. Loss of Toll signalling suppresses ectopically and physiologically activated JNK signalling-induced cell death. Our epistasis analysis suggests that the Toll pathway acts as a downstream modulator for JNK-dependent cell death. In addition, gain of JNK signalling results in Toll pathway activation, revealed by stimulated transcription of Drosomycin (Drs) and increased cytoplasm-to-nucleus translocation of Dorsal. Furthermore, the Spätzle (Spz) family ligands for the Toll receptor are transcriptionally upregulated by activated JNK signalling in a non-cell-autonomous manner, providing a molecular mechanism for JNK-induced Toll pathway activation. Finally, gain of Toll signalling exacerbates JNK-mediated cell death and promotes cell death independent of caspases. Thus, we have identified another important function for the evolutionarily conserved Toll pathway, in addition to its well-studied roles in embryonic dorso-ventral patterning and innate immunity.
Keywords: Drosophila; Eiger; Toll; c-Jun N-terminal kinase; cell death.
Figures



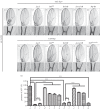


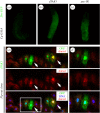
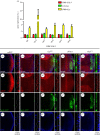

References
-
- Hashimoto C, Hudson KL, Anderson KV. 1988. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal–ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell 52, 269–279. (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(88)90516-8) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Steward R. 1987. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science 238, 692–694. (doi:10.1126/science.3118464) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roth S, Hiromi Y, Godt D, Nusslein-Volhard C. 1991. cactus, a maternal gene required for proper formation of the dorsoventral morphogen gradient in Drosophila embryos. Development 112, 371–388. - PubMed
-
- Letsou A, Alexander S, Orth K, Wasserman SA. 1991. Genetic and molecular characterization of tube, a Drosophila gene maternally required for embryonic dorsoventral polarity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 810–814. (doi:10.1073/pnas.88.3.810) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

