Distinctive clinical characteristics of malignant mesothelioma in young patients
- PMID: 26202904
- PMCID: PMC4599306
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4414
Distinctive clinical characteristics of malignant mesothelioma in young patients
Abstract
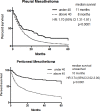
Although considered a disease of the elderly, a subset of patients with mesothelioma are young (<40 years). The goal of this study was to understand their characteristics and outcomes. The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database was used to extract mesothelioma cases (1990-2010). We modeled Kaplan-Meyer survival curves stratified by site of disease, and age of presentation. 2% (207 of 12345) of mesothelioma patients are young. Sex distribution is comparable among the young (51% males, 49% females); males predominated (78%, 22%) in the older cohort. Frequency of pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma are similar in the young (47%, 48% respectively); pleural disease predominated in the old (90%, 9%). Cancer-directed surgeries are more frequent in the young. Regardless of histologic subtype, young patients with pleural (11 vs. 8 months) and peritoneal (not reached vs. 10 months) mesothelioma had significantly improved overall survival. In multivariate analysis, younger age was an independent prognostic factor. Although rare, mesothelioma do occur in the young; their characteristics are distinct from those of older patients. Further studies are needed to understand the interplay between genetic susceptibility and mineral fiber carcinogenesis in the pathogenesis of mesothelioma in the young.
Keywords: SEER analysis; asbestos; incidence among the young; mesothelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rodriguez D, Cheung MC, Housri N, Koniaris LG. Malignant abdominal mesothelioma: defining the role of surgery. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J, Denham C, Kaukel E, Ruffie P, Gatzemeier U, Boyer M, Emri S, Manegold C, Niyikiza C, Paoletti P. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:2636–2644. - PubMed
-
- Janne PA, Wozniak AJ, Belani CP, Keohan ML, Ross HJ, Polikoff JA, Mintzer DM, Taylor L, Ashland J, Ye Z, Monberg MJ, Obasaju CK. Open-label study of pemetrexed alone or in combination with cisplatin for the treatment of patients with peritoneal mesothelioma: outcomes of an expanded access program. Clin Lung Cancer. 2005;7:40–46. - PubMed
-
- Carteni G, Manegold C, Garcia GM, Siena S, Zielinski CC, Amadori D, Liu Y, Blatter J, Visseren-Grul C, Stahel R. Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma-Results from the International Expanded Access Program using pemetrexed alone or in combination with a platinum agent. Lung Cancer. 2009;64:211–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical