Pulmonary hemodynamic profile in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 26203238
- PMCID: PMC4507485
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S78180
Pulmonary hemodynamic profile in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Pulmonary hemodynamic profile in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [Corrigendum].Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015 Nov 4;10:2377. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S96102. eCollection 2015. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015. PMID: 26604735 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Few data are available in regards to the prevalence of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in the broad spectrum of COPD. This study was aimed at assessing the prevalence of PH in a cohort of COPD patients across the severity of airflow limitation, and reporting the hemodynamic characteristics at rest and during exercise.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis on COPD patients who underwent right-heart catheterization in our center with measurements obtained at rest (n=139) and during exercise (n=85). PH was defined as mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) ≥25 mmHg and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure <15 mmHg. Exercise-induced PH (EIPH) was defined by a ratio of ΔmPAP/Δcardiac output >3.
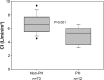
Results: PH was present in 25 patients (18%). According to the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) classification, PH prevalence in GOLD 2 was 7% (3 patients); 25% (14 patients) in GOLD 3; and 22% (8 patients) in GOLD 4. Severe PH (mPAP ≥35 mmHg) was identified in four patients (2.8%). Arterial partial oxygen pressure was the outcome most strongly associated with PH (r=-0.29, P<0.001). EIPH was observed in 60 patients (71%) and had a similar prevalence in both GOLD 2 and 3, and was present in all GOLD 4 patients. Patients with PH had lower cardiac index during exercise than patients without PH (5.0±1.2 versus 6.7±1.4 L/min/m(2), respectively; P=0.001).
Conclusion: PH has a similar prevalence in COPD patients with severe and very-severe airflow limitation, being associated with the presence of arterial hypoxemia. In contrast, EIPH is highly prevalent, even in moderate COPD, and might contribute to limiting exercise tolerance.
Keywords: GOLD; cardiac index; pulmonary hypertension; right heart catheterization.
Figures

References
-
- Barberà JA, Peinado VI, Santos S. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J. 2003;21(5):892–905. - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Barberà JA, Channick RN, et al. Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of non-pulmonary arterial hypertension pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(1 Suppl):S85–S96. - PubMed
-
- Seeger W, Adir Y, Barberà JA, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung diseases. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25 Suppl):D109–D116. - PubMed
-
- Oswald-Mammosser M, Apprill M, Bachez P, Ehrhart M, Weitzenblum E. Pulmonary hemodynamics in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease of the emphysematous type. Respiration. 1991;58(5–6):304–310. - PubMed

