Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren Syndrome Patients With Refractory Thrombocytopenia: A Retrospective Study of 21 Cases
- PMID: 26203828
- PMCID: PMC4539196
- DOI: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000273
Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Sjögren Syndrome Patients With Refractory Thrombocytopenia: A Retrospective Study of 21 Cases
Abstract
Objective: Recent studies suggested a potential of rituximab (RTX) in treating autoimmune thrombocytopenia (AITP) secondary to autoimmune diseases. In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the efficacy and safety of RTX therapy in patients with refractory AITP secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren syndrome (SS).
Methods: Twenty-one SLE and/or SS patients with treatment-resistant AITP were treated once or repeatedly with RTX at the Rheumatology Clinic Renji Hospital, during the period March 2012 to June 2014. Clinical and laboratory variables recorded at every follow-up visit were analyzed.
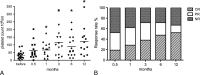
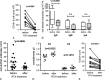
Results: The median age of all patients was 37.05 ± 3.15 years (range, 13-67 years; 20 female and 1 male). The median AITP duration before RTX treatment was 5.46 years. Previous treatments of 21 patients included immunosuppressive agents such as corticosteroids (n = 19), cyclosporine (n = 9), mycophenolate mofetil (n = 2), methotrexate (n = 3), cyclophosphamide (n = 2), vincristine (n = 3), and hydroxychloroquine (n = 15), and 7 patients received concomitantly intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Two patients had undergone splenectomy without improvement. Seventeen patients (80.95%) were treated repeatedly with RTX during the follow-up period. The overall response rate to RTX treatment (including complete response, 52.38%; partial response, 28.57%) was 80.95%. A significant increase (P < 0.05) of platelet counts was seen after 1 month (median, 32.24 × 10/mL vs 66.53 × 10/mL). Relapses occurred mostly during the first 9 months, and maintaining duration of response was 10.27 months (range, 2-17 months) on average after the first RTX infusion. Antiplatelet antibodies, especially IgG isotype, decreased significantly (P < 0.05) after RTX treatment. No adverse effects were observed among 15 patients (71.4%); however, 2 cases died of severe pneumonia, and another developed lymphoma.
Conclusions: Rituximab is an additional potent therapeutic treatment option for SLE and SS patients with AITP refractory to conventional immunosuppressive treatments. For most patients, RTX was safe and well tolerated.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar S, Benseler SM, Kirby-Allen M, et al. B-cell depletion for autoimmune thrombocytopenia and autoimmune hemolytic anemia in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatrics. 2009; 123: e159– e163. - PubMed
-
- Sultan SM, Begum S, Isenberg DA. Prevalence, patterns of disease and outcome in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus who develop severe haematological problems. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003; 42: 230– 234. - PubMed
-
- Nossent JC, Swaak AJ. Prevalence and significance of haematological abnormalities in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1991; 80: 605– 612. - PubMed
-
- Mok CC, Lee KW, Ho CT, et al. A prospective study of survival and prognostic indicators of systemic lupus erythematosus in a southern Chinese population. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000; 39: 399– 406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

