Solution-Processed Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Ultralow Driving Voltage and Very High Power Efficiency
- PMID: 26204810
- PMCID: PMC4513343
- DOI: 10.1038/srep12487
Solution-Processed Phosphorescent Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Ultralow Driving Voltage and Very High Power Efficiency
Abstract
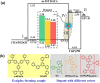
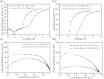
To realize power efficient solution-processed phosphorescent organic light-emitting diodes (s-PhOLEDs), the corresponding high driving voltage issue should be well solved. To solve it, efforts have been devoted to the exploitation of novel host or interfacial materials. However, the issues of charge trapping of phosphor and/or charge injection barrier are still serious, largely restraining the power efficiency (PE) levels. Herein, with the utilization of an exciplex-forming couple 4, 4', 4″-tris[3-methylphenyl(phenyl)amino]triphenylamine (m-MTDATA) and 1,3,5-tri(m-pyrid-3-yl-phenyl)benzene (TmPyPB), the efficient charge injection and transporting, barrier-free hole-electron recombination for the formation of the interfacial exciplex, and elimination of charge traps of phosphors in the emissive layer are realized simultaneously, resulting in a turn-on voltage of 2.36 V, a record high PE of 97.2 lm W(-1), as well as extremely low driving voltage of 2.60 V at 100 cd m(-2), 3.03 V at 1000 cd m(-2) and 4.08 V at 10000 cd m(-2). This report is the first time that the PE performance of s-PhOLED approaches 100 lm W(-1) high level, even superior to the corresponding state-of-the-art performance of the same color vacuum-deposited PhOLED (v-PhOLED) counterpart. We anticipate this report opens a new avenue for achieving power efficient monochromatic and white s-PhOLEDs with simple structures.
Figures


References
-
- Reineke S., Thomschke M., Luessem B. & Leo K. White organic light-emitting diodes: status and perspective. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 1245–1293 (2013).
-
- Su S. J., Gonmori E., Sasabe H. & Kido J. Highly efficient organic blue- and white-light-emitting devices having a carrier- and exciton-confining structure for reduced efficiency roll-off. Adv. Mater. 20, 4189–4194 (2008).
-
- Wang Q. et al. A non-doped phosphorescent organic light-emitting device with above 31% external quantum efficiency. Adv. Mater. 26, 8107–8113 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Sasabe H. et al. Extremely low operating voltage green phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 23, 5550–5555 (2013).
-
- Lee J. H. et al. An exciplex forming host for highly efficient blue organic light emitting diodes with low driving voltage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 361–366 (2015).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

