Increased inflammation but similar physical composition and function in older-aged, HIV-1 infected subjects
- PMID: 26204934
- PMCID: PMC4513956
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-015-0106-z
Increased inflammation but similar physical composition and function in older-aged, HIV-1 infected subjects
Abstract
Background: Systemic immune activation (inflammation) and immunosenescence develop in some people with advancing age. This process, known as "inflamm-aging," is associated with physical frailty and sarcopenia. Meanwhile, successful antiretroviral therapy has led to a growing number of older HIV-1-infected individuals who face both age-related and HIV-1-related inflammation, which may synergistically promote physical decline, including frailty and sarcopenia. The purpose of our study was to determine if inflammation during treated HIV-1 infection worsens physical impairment in older individuals.
Methods: We determined the severity of HIV-associated inflammation and physical performance (strength and endurance) in 21 older HIV-infected individuals (54-69 years) receiving suppressive antiretroviral therapy, balanced for confounding variables including age, anthropometrics, and co-morbidities with 10 uninfected control individuals. Biomarkers for microbial translocation (lipopolysaccharide [LPS]), inflammation (soluble CD14 [sCD14], osteopontin, C-reactive protein [CRP], interleukin-6 [IL-6], soluble ICAM-1 [sICAM-1] and soluble VCAM-1 [sVCAM-1]), and coagulopathy (D-dimer) were assayed in plasma. Activation phenotypes of CD4(+)T cells, CD8(+) T cells and monocytes were measured by flow cytometry. Physical performance was measured by 400 m walking speed, a short physical performance battery [SPPB], and lower extremity muscle strength and fatigue.
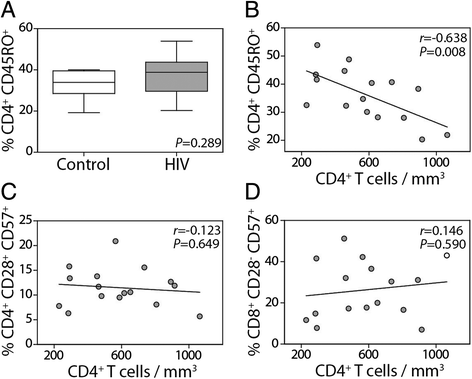
Results: Overall physical function was similar in the uninfected and HIV-infected groups. Compared to uninfected individuals, the HIV-infected group had elevated levels of sCD14 (P < 0.001), CRP (P < 0.001) and IL-6 (P = 0.003) and an increased frequency of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells with an immunosenescent CD57(+) phenotype (P = 0.004 and P = 0.043, respectively). Neither plasma inflammatory biomarkers nor CD57(+) T cells correlated with CD4(+) T cell counts. Furthermore, none of the elevated inflammatory biomarkers in the HIV-infected subjects were associated with any of the physical performance results.
Conclusions: When age-related co-morbidities were carefully balanced between the uninfected and HIV-infected groups, no evidence of inflammation-associated physical impairment was detected. Despite careful balancing for age, BMI, medications and co-morbidities, the HIV-infected group still displayed evidence of significant chronic inflammation, including elevated sCD14, CRP, IL-6 and CD57(+) T cells, although the magnitude of this inflammation was unrelated to physical impairment.
Figures


References
-
- Franceschi C. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014;69(Suppl 1):S4-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

