Identifying novel hypoxia-associated markers of chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 26205780
- PMCID: PMC4513971
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1539-8
Identifying novel hypoxia-associated markers of chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
Abstract
Background: Ovarian cancer is associated with poor long-term survival due to late diagnosis and development of chemoresistance. Tumour hypoxia is associated with many features of tumour aggressiveness including increased cellular proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, increased invasion and metastasis, and chemoresistance, mostly mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α. While HIF-1α has been associated with platinum resistance in a variety of cancers, including ovarian, relatively little is known about the importance of the duration of hypoxia. Similarly, the gene pathways activated in ovarian cancer which cause chemoresistance as a result of hypoxia are poorly understood. This study aimed to firstly investigate the effect of hypoxia duration on resistance to cisplatin in an ovarian cancer chemoresistance cell line model and to identify genes whose expression was associated with hypoxia-induced chemoresistance.
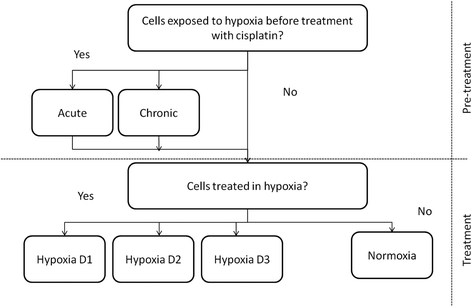
Methods: Cisplatin-sensitive (A2780) and cisplatin-resistant (A2780cis) ovarian cancer cell lines were exposed to various combinations of hypoxia and/or chemotherapeutic drugs as part of a 'hypoxia matrix' designed to cover clinically relevant scenarios in terms of tumour hypoxia. Response to cisplatin was measured by the MTT assay. RNA was extracted from cells treated as part of the hypoxia matrix and interrogated on Affymetrix Human Gene ST 1.0 arrays. Differential gene expression analysis was performed for cells exposed to hypoxia and/or cisplatin. From this, four potential markers of chemoresistance were selected for evaluation in a cohort of ovarian tumour samples by RT-PCR.
Results: Hypoxia increased resistance to cisplatin in A2780 and A2780cis cells. A plethora of genes were differentially expressed in cells exposed to hypoxia and cisplatin which could be associated with chemoresistance. In ovarian tumour samples, we found trends for upregulation of ANGPTL4 in partial responders and down-regulation in non-responders compared with responders to chemotherapy; down-regulation of HER3 in partial and non-responders compared to responders; and down-regulation of HIF-1α in non-responders compared with responders.
Conclusion: This study has further characterized the relationship between hypoxia and chemoresistance in an ovarian cancer model. We have also identified many potential biomarkers of hypoxia and platinum resistance and provided an initial validation of a subset of these markers in ovarian cancer tissues.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SENP1 desensitizes hypoxic ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin by up-regulating HIF-1α.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 9;5:16396. doi: 10.1038/srep16396. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26548925 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells by targeting HIF-1-regulated cancer metabolism.Cancer Lett. 2016 Apr 1;373(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.009. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26801746 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between p53 and Ras signaling controls cisplatin resistance via HDAC4- and HIF-1α-mediated regulation of apoptosis and autophagy.Theranostics. 2019 Jan 30;9(4):1096-1114. doi: 10.7150/thno.29673. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 30867818 Free PMC article.
-
The role of membrane transporters in ovarian cancer chemoresistance and prognosis.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017 Jul;13(7):741-753. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2017.1332179. Epub 2017 May 29. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28511565 Review.
-
The contribution of copper efflux transporters ATP7A and ATP7B to chemoresistance and personalized medicine in ovarian cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110401. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110401. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32570116 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of heregulins, HER3, and HER4 as potential therapeutic targets in cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(51):89284-89306. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18467. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of CYLD by HER3 confers ovarian cancer platinum resistance via inhibiting apoptosis and by inducing drug efflux.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 Feb 26;14(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00620-z. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40012003 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Mediated Decrease of Ovarian Cancer Cells Reaction to Treatment: Significance for Chemo- and Immunotherapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 14;21(24):9492. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249492. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33327450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ovarian tumor microenvironment contributes to tumor progression and chemoresistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 17;7:53. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.111. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39802952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing the Secretomes of Chemorefractory and Chemoresistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Populations.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;14(6):1418. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061418. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326569 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Globocan: Population fact sheets. Estimated age-standardised incidence and mortality rates: women [http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact_sheets_population.aspx]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

