miR-216a rescues dexamethasone suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 26206089
- PMCID: PMC4816120
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2015.99
miR-216a rescues dexamethasone suppression of osteogenesis, promotes osteoblast differentiation and enhances bone formation, by regulating c-Cbl-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway
Abstract
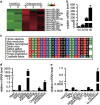
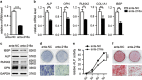
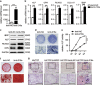
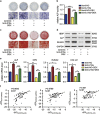
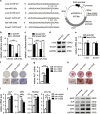
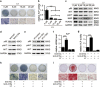
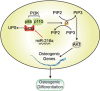
Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone mass, leading to an increased risk of fractures or broken bones. Bone formation is mediated by recruiting mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms that regulate MSC differentiation into osteoblasts is of great importance for the development of anabolic therapies for osteoporosis and other bone metabolism-related diseases. microRNAs (miRNAs) have been reported to have crucial roles in bone development, osteogenic differentiation and osteoporosis pathophysiology. However, to date, only a few miRNAs have been reported to enhance osteogenesis and regulate the suppressive effect of glucocorticoids on osteogenic differentiation. In this study, we discovered that miR-216a, a pancreatic-specific miRNA, was significantly upregulated during osteogenic differentiation in human adipose-derived MSCs (hAMSCs). The expression of miR-216a was positively correlated with the expression of bone formation marker genes in clinical osteoporosis samples. Functional analysis demonstrated that miR-216a can markedly promote osteogenic differentiation of hAMSCs, rescue the suppressive effect of dexamethasone (DEX) on osteogenic differentiation in vitro and enhance bone formation in vivo. c-Cbl, a gene that encodes a RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligase, was identified as a direct target of miR-216a. Downregulation of c-Cbl by short hairpin RNAs can mimic the promotion effects of miR-216a and significantly rescue the suppressive effects of DEX on osteogenesis. Pathway analysis indicated that miR-216a regulation of osteogenic differentiation occurs via the c-Cbl-mediated phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. The recovery effects of miR-216a on the inhibition of osteogenesis by DEX were attenuated after blocking the PI3K pathway. Thus, our findings suggest that miR-216a may serve as a novel therapeutic agent for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and other bone metabolism-related diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed SF, Elmantaser M. Secondary osteoporosis. Endocr Dev 2009; 16: 170–190. - PubMed
-
- Canalis E, Delany AM. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid action in bone. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002; 966: 73–81. - PubMed
-
- Yun SI, Yoon HY, Jeong SY, Chung YS. Glucocorticoid induces apoptosis of osteoblast cells through the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Bone Miner Metab 2009; 27: 140–148. - PubMed
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999; 284: 143–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

