Targeted sequencing identifies associations between IL7R-JAK mutations and epigenetic modulators in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 26206799
- PMCID: PMC4591762
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2015.130179
Targeted sequencing identifies associations between IL7R-JAK mutations and epigenetic modulators in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
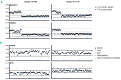
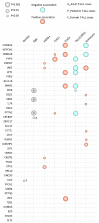
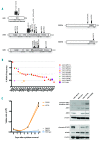
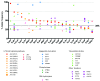
T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia is caused by the accumulation of multiple oncogenic lesions, including chromosomal rearrangements and mutations. To determine the frequency and co-occurrence of mutations in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, we performed targeted re-sequencing of 115 genes across 155 diagnostic samples (44 adult and 111 childhood cases). NOTCH1 and CDKN2A/B were mutated/deleted in more than half of the cases, while an additional 37 genes were mutated/deleted in 4% to 20% of cases. We found that IL7R-JAK pathway genes were mutated in 27.7% of cases, with JAK3 mutations being the most frequent event in this group. Copy number variations were also detected, including deletions of CREBBP or CTCF and duplication of MYB. FLT3 mutations were rare, but a novel extracellular mutation in FLT3 was detected and confirmed to be transforming. Furthermore, we identified complex patterns of pairwise associations, including a significant association between mutations in IL7R-JAK genes and epigenetic regulators (WT1, PRC2, PHF6). Our analyses showed that IL7R-JAK genetic lesions did not confer adverse prognosis in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cases enrolled in the UK ALL2003 trial. Overall, these results identify interconnections between the T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia genome and disease biology, and suggest a potential clinical application for JAK inhibitors in a significant proportion of patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Copyright© Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures

References
-
- Weng AP, Ferrando AA, Lee W, et al. Activating mutations of NOTCH1 in human T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Science. 2004;306(5694):269–271. - PubMed
-
- Aifantis I, Raetz E, Buonamici S. Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(5):380–390. - PubMed
-
- Hebert J, Cayuela JM, Berkeley J, Sigaux F. Candidate tumor-suppressor genes MTS1 (p16INK4A) and MTS2 (p15INK4B) display frequent homozygous deletions in primary cells from T- but not from B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Blood. 1994;84(12):4038–4044. - PubMed
-
- Soulier J, Clappier E, Cayuela J-M, et al. HOXA genes are included in genetic and biologic networks defining human acute T-cell leukemia (T-ALL). Blood. 2005;106(1):274–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

