A Longitudinal Examination of the Associations Between Shyness, Drinking Motives, Alcohol Use, and Alcohol-Related Problems
- PMID: 26207856
- PMCID: PMC4558315
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12799
A Longitudinal Examination of the Associations Between Shyness, Drinking Motives, Alcohol Use, and Alcohol-Related Problems
Abstract
Background: The current study evaluated the roles of drinking motives and shyness in predicting problem alcohol use over 2 years.
Methods: First-year college student drinkers (n = 818) completed assessments of alcohol use and related problems, shyness, and drinking motives every 6 months over a 2-year period.
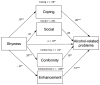
Results: Generalized linear mixed models indicated that shyness was associated with less drinking, but more alcohol-related problems. Further, shyness was associated with coping, conformity, and enhancement drinking motives, but was not associated with social drinking motives. However, when examining coping motives, moderation analyses revealed that social drinking motives were more strongly associated with coping motives among individuals higher in shyness. In addition, coping, conformity, and enhancement motives, but not social motives, mediated associations between shyness and alcohol-related problems over time. Finally, coping motives mediated the association between the interaction of shyness and social motives and alcohol-related problems.
Conclusions: Together, the results suggest that shy individuals may drink to reduce negative affect, increase positive affect, and fit in with others in social situations, which may then contribute to greater risk for subsequent alcohol-related problems.
Keywords: Conformity Motives; Coping Motives; Enhancement Motives; Social Anxiety; Social Motives.
Copyright © 2015 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protective behavioral strategy use and motivations for drinking: exploring Alternatives to Drinking strategies.Addict Behav. 2014 Feb;39(2):469-72. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.10.008. Epub 2013 Oct 9. Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24229844
-
Compounding risk: An examination of associations between spirituality/religiosity, drinking motives, and alcohol-related ambivalence among heavy drinking young adults.Addict Behav. 2016 Dec;63:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.06.026. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Addict Behav. 2016. PMID: 27393932 Free PMC article.
-
Impulsivity and drinking motives predict problem behaviours relating to alcohol use in university students.Addict Behav. 2014 Jan;39(1):289-96. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.10.024. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 24176824
-
The "Why" of Drinking Matters: A Meta-Analysis of the Association Between Drinking Motives and Drinking Outcomes.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jan;45(1):38-50. doi: 10.1111/acer.14518. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 33206387
-
Why do young people drink? A review of drinking motives.Clin Psychol Rev. 2005 Nov;25(7):841-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2005.06.002. Clin Psychol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16095785 Review.
Cited by
-
Shifts in alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic: early indications from Australia.Addiction. 2021 Jun;116(6):1381-1388. doi: 10.1111/add.15275. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Addiction. 2021. PMID: 33006789 Free PMC article.
-
Shyness and susceptibility to social influence: Stronger concordance between norms and drinking among shy individuals.Addict Behav. 2021 Aug;119:106922. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106922. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Addict Behav. 2021. PMID: 33838576 Free PMC article.
-
Parental Monitoring and Adolescent Problematic Mobile Phone Use: The Mediating Role of Escape Motivation and the Moderating Role of Shyness.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 25;17(5):1487. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051487. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32106623 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise and Alcohol Consumption: What We Know, What We Need to Know, and Why it is Important.Front Psychiatry. 2015 Nov 2;6:156. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00156. eCollection 2015. Front Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26578988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol acutely enhances decoding of positive emotions and emotional concern for positive stimuli and facilitates the viewing of sexual images.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Jan;234(1):41-51. doi: 10.1007/s00213-016-4431-6. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 27640999 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bruch M, Heimberg R, Harvey C, McCann M, Mahone M, Slavkin S. Shyness, alcohol expectancies, and alcohol use: Discovery of a suppressor effect. J Res Pers. 1992;26:137–149.
-
- Bruch M, Gorsky J, Collins T, Berger P. Shyness and sociability reexamined: A multicomponent analysis. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1989;57:904–915.
-
- Bruch M, Rivet K, Heimberg R, Levin M. Shyness, alcohol expectancies, and drinking behavior: Replication and extension of a suppressor effect. Pers Indiv Differ. 1997;22:193–200.
-
- Buckner J, Schmidt N, Eggleston A. Social anxiety and problematic alcohol consumption: The mediating role of drinking motives and situations. Behav Ther. 2006;37:381–391. - PubMed
-
- Buss AH. Shyness. Springer US; 1986. A theory of shyness; pp. 39–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

