Impact of TG4010 Vaccine on Health-Related Quality of Life in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Phase IIB Clinical Trial
- PMID: 26207902
- PMCID: PMC4514809
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132568
Impact of TG4010 Vaccine on Health-Related Quality of Life in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Phase IIB Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: This study describes the effect of TG4010 vaccine on Health related Quality of Life (HRQOL) in patients with stage IIIb and IV non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
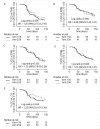
Methods: 148 patients with advanced NSCLC expressing MUC1 were randomly assigned to receive TG4010 plus chemotherapy or chemotherapy alone. HRQOL was assessed with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Lung (FACT-L) at baseline and every 6 weeks until disease progression. Time until definitive deterioration (TUDD) of the four well-being dimensions of the FACT-L physical (PWB), functional (FWB), emotional (EWB) and social well-being (SWB) and the Lung Cancer Subscale (LCS) domains were analyzed for a 5-point minimal clinically important difference.
Results: No difference of TUDD of HRQOL has been found between treatment arms. No prognostic factors have been found to have a significant impact on the TUDD of PWB, SWB and LCS domains. The gender, the performance status and the smoking habits seemed to be associated with a shorter TUDD of EWB domain. The smokers and the former smokers seemed to present a shorter TUDD of FWB domain.
Conclusion: This study suggests that adding therapeutic vaccination with TG4010 to standard chemotherapy in patients with advanced NSCLC is associated with a similar evolution in HRQOL compared to chemotherapy alone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer. Adopted on May 16, 1997 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15: 2996–3018. - PubMed
-
- Gridelli C, Perrone F, Nelli F, Ramponi S, De Marinis F. Quality of life in lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2001; 12 Suppl 3: S21–25. - PubMed
-
- Rossi A, Maione P, Colantuoni G, Ferrara C, Rossi E, Guerriero C, et al. Recent developments of targeted therapies in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2009; 6: 91–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

