LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer
- PMID: 26208723
- PMCID: PMC4544839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.07.001
LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer
Abstract
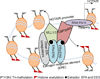
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are emerging classes of regulatory RNA that play key roles in various cellular and physiological processes such as in gene regulation, chromatin dynamics, cell differentiation, and development. NcRNAs are dysregulated in a variety of human disorders including cancers, neurological disorders, and immunological disorders. The mechanisms through which ncRNAs regulate various biological processes and human diseases still remain elusive. HOX antisense intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) is a recently discovered long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that plays critical role in gene regulation and chromatin dynamics, appears to be misregulated in a variety of cancers. HOTAIR interacts with key epigenetic regulators such as histone methyltransferase PRC2 and histone demethylase LSD1 and regulates gene silencing. Here, we have reviewed recent advancements in understanding the functions and regulation of HOTAIR and its association with cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: Cancer; Epigenetics; HOTAIR; LncRNA; Non-coding RNA.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

