Network-Based Integration of GWAS and Gene Expression Identifies a HOX-Centric Network Associated with Serous Ovarian Cancer Risk
- PMID: 26209509
- PMCID: PMC4592449
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-1270
Network-Based Integration of GWAS and Gene Expression Identifies a HOX-Centric Network Associated with Serous Ovarian Cancer Risk
Abstract
Background: Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have so far reported 12 loci associated with serous epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) risk. We hypothesized that some of these loci function through nearby transcription factor (TF) genes and that putative target genes of these TFs as identified by coexpression may also be enriched for additional EOC risk associations.
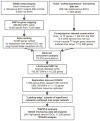
Methods: We selected TF genes within 1 Mb of the top signal at the 12 genome-wide significant risk loci. Mutual information, a form of correlation, was used to build networks of genes strongly coexpressed with each selected TF gene in the unified microarray dataset of 489 serous EOC tumors from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Genes represented in this dataset were subsequently ranked using a gene-level test based on results for germline SNPs from a serous EOC GWAS meta-analysis (2,196 cases/4,396 controls).
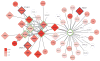
Results: Gene set enrichment analysis identified six networks centered on TF genes (HOXB2, HOXB5, HOXB6, HOXB7 at 17q21.32 and HOXD1, HOXD3 at 2q31) that were significantly enriched for genes from the risk-associated end of the ranked list (P < 0.05 and FDR < 0.05). These results were replicated (P < 0.05) using an independent association study (7,035 cases/21,693 controls). Genes underlying enrichment in the six networks were pooled into a combined network.
Conclusion: We identified a HOX-centric network associated with serous EOC risk containing several genes with known or emerging roles in serous EOC development.
Impact: Network analysis integrating large, context-specific datasets has the potential to offer mechanistic insights into cancer susceptibility and prioritize genes for experimental characterization.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Fasching reports receiving commercial research support from Amgen and Novartis and honoraria from speakers’ bureaus from Amgen, Novartis, Pfizer, Celgene, Roche, and GSK. Dr. Menon reports having a commercial research grant from and ownership interest in Abcodia.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA136924/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080742/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA074850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA092044/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA174664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA115195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076016/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA095666/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA069417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA050385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA172404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC067010/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA159981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA067262/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA106414/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA070867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA184415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA113148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 CA138563/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058860/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA105009/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC035137/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA076292/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA064277/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA083918/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA122443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA143047/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES013678/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009001/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA149429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA017054/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CN025403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA049449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063682/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19-CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA124435/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA136393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 CA165638/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126841/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15960/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA114343/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16561/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

