Postlobectomy Early Complications
- PMID: 26210931
- PMCID: PMC4606870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thorsurg.2015.04.003
Postlobectomy Early Complications
Abstract
Immediate postoperative complications are common after lobectomy. The most effective management of postoperative crises is prevention, which starts with preoperative preparation and patient screening. There are many factors that can be controlled and improved by the patient. Equally important is patient selection, which is influenced by pulmonary function tests, cardiopulmonary reserve, and preexisting comorbidities. After the operation, the care team can also greatly improve outcomes with aggressive cardiopulmonary therapies, ambulation, vigilant monitoring, and frequent assessments of the patient. Prevention strategies can minimize risks; however, when they occur, a proactive approach may minimize the long-term sequelae.
Keywords: Air leak; Atrial fibrillation; Chylothorax; Hemorrhage; Nerve injury; Pneumonia/mucous plugging; Right middle lobe torsion.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
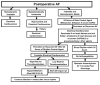
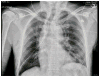
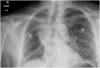
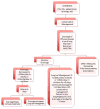
References
-
- Rosen JE, Hancock JG, Kim AW, et al. Predictors of mortality after surgical management of lung cancer in the national cancer database. Ann of Thorac Surg. 2014 Article in Press. - PubMed
-
- Berry MF, Hanna J, Tong BC, et al. Risk factors for morbidity after lobectomy for lung cancer in elderly patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88(4):1093–9. - PubMed
-
- Allen MS, Darling GE, Pechet TT, et al. Morbidity and mortality of major pulmonary resections in patients with early-stage lung cancer: initial results of the randomized, prospective ACOSOG Z0030 trial. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2006;81(3):1013–9. - PubMed
-
- Rice TW, Kirby TJ. Prolonged air leak. Chest Surg Clin North Am. 1992;2:802–811.
-
- Cerfolio RJ, Tummula RP, Holman WL, et al. A prospective algorithm for the management of air leaks after pulmonary resection. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998;66:1726–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

