Conformational Differences between Open and Closed States of the Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Complex
- PMID: 26212456
- PMCID: PMC4534855
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.033
Conformational Differences between Open and Closed States of the Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Complex
Abstract
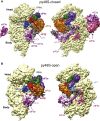
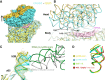
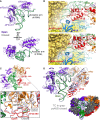
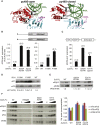
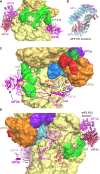
Translation initiation in eukaryotes begins with the formation of a pre-initiation complex (PIC) containing the 40S ribosomal subunit, eIF1, eIF1A, eIF3, ternary complex (eIF2-GTP-Met-tRNAi), and eIF5. The PIC, in an open conformation, attaches to the 5' end of the mRNA and scans to locate the start codon, whereupon it closes to arrest scanning. We present single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) reconstructions of 48S PICs from yeast in these open and closed states, at 6.0 Å and 4.9 Å, respectively. These reconstructions show eIF2β as well as a configuration of eIF3 that appears to encircle the 40S, occupying part of the subunit interface. Comparison of the complexes reveals a large conformational change in the 40S head from an open mRNA latch conformation to a closed one that constricts the mRNA entry channel and narrows the P site to enclose tRNAi, thus elucidating key events in start codon recognition.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Algire M.A., Maag D., Lorsch J.R. Pi release from eIF2, not GTP hydrolysis, is the step controlled by start-site selection during eukaryotic translation initiation. Mol. Cell. 2005;20:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Aylett C.H., Boehringer D., Erzberger J.P., Schaefer T., Ban N. Structure of a yeast 40S-eIF1-eIF1A-eIF3-eIF3j initiation complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015;22:269–271. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shem A., Garreau de Loubresse N., Melnikov S., Jenner L., Yusupova G., Yusupov M. The structure of the eukaryotic ribosome at 3.0 Å resolution. Science. 2011;334:1524–1529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

