High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T is more helpful in detecting peri-operative myocardial injury and apoptosis during coronary artery bypass graft surgery
- PMID: 26212819
- PMCID: PMC4780022
- DOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2015-052
High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T is more helpful in detecting peri-operative myocardial injury and apoptosis during coronary artery bypass graft surgery
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether there is a correlation between cardiac markers and peri-operative myocardial injury (PMI) and apoptosis in coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery and to compare the efficacy of cardiac markers to detect PMI.
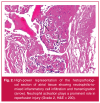
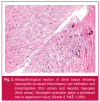
Methods: The study population consisted of 37 patients (24 male, 13 female, mean age 63.4 ± 8.9 years) undergoing elective CABG. Arterial and coronary sinus blood samples were collected just before aortic cross-clamping (pre-ACC) and after aortic declamping (post-ACC). Creatine kinase-MB isoenzyme (CK-MB) activity, and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT), creatine kinase-MB isoenzyme mass (CK-MB mass) and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) concentrations were measured in blood samples. Myocardial injury and apoptosis were examined in atrial biopsies.
Results: CABG caused PMI and apoptosis in all cases. Concentrations and net releases of cardiac markers significantly increased after aortic declamping (p < 0.001 for CK-MB and CK-MB mass, p < 0.01 for cTnI, p < 0.05 for hs-cTnT). A positive correlation was found between apoptotic index (r = 0.611, p < 0.001 for cTnI; r = 0.806, p < 0.001 for hs-cTnT), myocardial injury score (r = 0.544, p < 0.001 for cTnI; r = 0.719, p < 0.001 for hs-cTnT) and cTnI and hs-cTnT values in the post-ACC period. A positive correlation was found between apoptotic index (r = 0.507, p < 0.001), myocardial injury score (r = 0.416, p = 0.010) and net release of hs-cTnT. Furthermore, a positive correlation was found between aortic cross-clamp (ACC) time (r = 0.448, p = 0.007), cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) time (r = 0.342, p = 0.047) and net release of hs-cTnT.
Conclusion: Although both cTnI and hs-cTnT may be specific and efficacious markers of myocardial apoptosis and injury occurring during CABG with CPB, hs-cTnT may be a more useful marker than cTnI to detect peri-operative myocardial apoptosis and injury.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of cardiac troponin I versus T and creatine kinase MB after coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with and without perioperative myocardial infarction.Herz. 2004 Nov;29(7):658-64. doi: 10.1007/s00059-004-2543-y. Herz. 2004. PMID: 15580320 Clinical Trial.
-
Sialic acid or troponin T to detect perioperative myocardial damage in patients undergoing elective coronary artery bypass grafting.Circ J. 2002 Nov;66(11):1019-23. doi: 10.1253/circj.66.1019. Circ J. 2002. PMID: 12419933
-
CD11b may be a less satisfactory indicator for cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury in coronary artery bypass graft surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass than cardiac troponin I.J Clin Anesth. 2005 May;17(3):158-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2004.06.008. J Clin Anesth. 2005. PMID: 15896579
-
High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I and T Kinetics Differ following Coronary Bypass Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Chem. 2022 Dec 6;68(12):1564-1575. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvac152. Clin Chem. 2022. PMID: 36366960
-
Laboratory diagnosis of patients with acute chest pain.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2000 Mar;38(3):187-97. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2000.027. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2000. PMID: 10905753 Review.
Cited by
-
Myocardial Protecting Role of Glutamine in Patients with Low Ejection Fraction Undergoing Elective On-Pump Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022 Apr 5;18:219-231. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S361298. eCollection 2022. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35411147 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Empagliflozin improves high-sensitive cardiac troponin-I and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease: a post-hoc analysis of EMPA-CARD Trial.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Sep 22;22(2):1723-1730. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01305-2. eCollection 2023 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 37975102 Free PMC article.
-
Release Profile of Cardiac Troponin T and Risk Factors of Postoperative Myocardial Injury in Patients Undergoing CABG.Int J Gen Med. 2021 Jun 15;14:2541-2551. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S315691. eCollection 2021. Int J Gen Med. 2021. PMID: 34163222 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Cardioplegic Solutions in Coronary Bypass Surgery Over Autophagy and Apoptosis Mechanisms.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Jun;120(7):e20220479. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220479. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37466618 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
-
Correlation Between Cardiac Index, Plasma Troponin I, Myocardial Histopathology, CPB and AoX Duration in Glutamine versus No Glutamine Administered Patients with Low Ejection Fraction Undergoing Elective On-Pump CABG Surgery: Secondary Analysis of an RCT.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2023 Feb 28;19:93-101. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S399925. eCollection 2023. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2023. PMID: 36880009 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Nicolini F, Beghi C, Muscari C, Agostinelli A, Maria Budillon A, Spaggiari I. et al. Myocardial protection in adult cardiac surgery: current options and future challenges. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;24:986–993. - PubMed
-
- Buckberg GD. Myocardial protection: entering the new millennium. J Card Surg. 2002;17:447–450. - PubMed
-
- Yau TM, Weisel RD, Mickle DA, Komeda M, Ivanov J, Carson S. et al. Alternative techniques of cardioplegia. Circulation. 1992;Suppl 2:377–384. - PubMed
-
- Benoit MO, Paris M, Silleran J, Fiemeyer A, Moatti N. Cardiac troponin I: its contribution to the diagnosis of perioperative myocardial infarction and various complications of cardiac surgery. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1880–1886. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

