In Vivo Integrity and Biological Fate of Chelator-Free Zirconium-89-Labeled Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
- PMID: 26213260
- PMCID: PMC4550540
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5b00526
In Vivo Integrity and Biological Fate of Chelator-Free Zirconium-89-Labeled Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
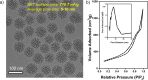
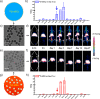
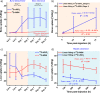
Traditional chelator-based radio-labeled nanoparticles and positron emission tomography (PET) imaging are playing vital roles in the field of nano-oncology. However, their long-term in vivo integrity and potential mismatch of the biodistribution patterns between nanoparticles and radio-isotopes are two major concerns for this approach. Here, we present a chelator-free zirconium-89 ((89)Zr, t1/2 = 78.4 h) labeling of mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN) with significantly enhanced in vivo long-term (>20 days) stability. Successful radio-labeling and in vivo stability are demonstrated to be highly dependent on both the concentration and location of deprotonated silanol groups (-Si-O(-)) from two types of silica nanoparticles investigated. This work reports (89)Zr-labeled MSN with a detailed labeling mechanism investigation and long-term stability study. With its attractive radio-stability and the simplicity of chelator-free radio-labeling, (89)Zr-MSN offers a novel, simple, and accurate way for studying the in vivo long-term fate and PET image-guided drug delivery of MSN in the near future.
Keywords: chelator-free radio-labeling; mesoporous silica nanoparticle; positron emission tomography; zirconium-89.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiolabeling Silica-Based Nanoparticles via Coordination Chemistry: Basic Principles, Strategies, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Mar 20;51(3):778-788. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00635. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29489335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and biodistribution of multiple 89Zr-labeled pore-expanded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for PET.Nanoscale. 2014 May 7;6(9):4928-35. doi: 10.1039/c3nr06800e. Nanoscale. 2014. PMID: 24675844
-
Intrinsic radiolabeling of Titanium-45 using mesoporous silica nanoparticles.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Jun;38(6):907-913. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.1. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 28414201 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the octadentate bifunctional chelator DFO*-pPhe-NCS and the clinically used hexadentate bifunctional chelator DFO-pPhe-NCS for 89Zr-immuno-PET.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017 Feb;44(2):286-295. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3499-x. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017. PMID: 27573793 Free PMC article.
-
89Zr-Immuno-Positron Emission Tomography in Oncology: State-of-the-Art 89Zr Radiochemistry.Bioconjug Chem. 2017 Sep 20;28(9):2211-2223. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00325. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Bioconjug Chem. 2017. PMID: 28767228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biodistribution and PET imaging of 89-zirconium labeled cerium oxide nanoparticles synthesized with several surface coatings.Nanomedicine. 2018 Jun;14(4):1429-1440. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 8. Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29641981 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeling Silica-Based Nanoparticles via Coordination Chemistry: Basic Principles, Strategies, and Applications.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Mar 20;51(3):778-788. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00635. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29489335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The new era of nanotechnology, an alternative to change cancer treatment.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Sep 27;11:2871-2890. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S142337. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 29033548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Approaches to Nanoparticle Labeling: A Review of Fluorescent, Radiological, and Metallic Techniques.Environ Health (Wash). 2023 Jun 21;1(2):75-89. doi: 10.1021/envhealth.3c00034. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. Environ Health (Wash). 2023. PMID: 39473584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesoporous silicas in materials engineering: Nanodevices for bionanotechnologies.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Oct 21;17:100472. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100472. eCollection 2022 Dec 15. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36340591 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim D. W. Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry for Fluorine-18 Labeling Protocols under Physiologically Friendly Reaction Condition. J. Fluorine Chem. 2015, 174, 142–14710.1016/j.jfluchem.2014.11.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

