Phase 1 safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic study of single ascending doses of XM17 (recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone) in downregulated healthy women
- PMID: 26213478
- PMCID: PMC4509534
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S83418
Phase 1 safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic study of single ascending doses of XM17 (recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone) in downregulated healthy women
Abstract
Background: XM17 is a recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone (follitropin alfa) for stimulation of multifollicular development in women undergoing controlled ovarian hyper-stimulation during assisted reproductive therapy and for treatment of anovulation. Manufactured using Chinese hamster ovary cells transfected with the human follicle-stimulating hormone gene, XM17 has an identical amino acid sequence to that of the human protein as well as to those of the other approved recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone products. Glycosylation patterns may differ slightly between products. The objectives of this first-in-human study were to assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and dose-proportionality of single ascending subcutaneous doses of XM17 in healthy young female volunteers.
Methods: Endogenous follicle-stimulating hormone was downregulated by implanting a 1-month depot of goserelin acetate 3.6 mg on day 0 in eligible subjects. On day 14 of the experimental period, subjects received one of four ascending doses of XM17. Blood sampling to obtain the pharmacokinetic profile of XM17 was done at frequent intervals until 168 hours post-dose.
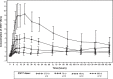
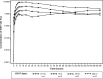
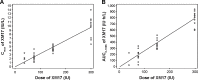
Results: Following downregulation of endogenous follicle-stimulating hormone to <4 IU/L, 40 subjects (of mean age 29±5.4 years) received single subcutaneous doses of 37.5 (n=4, pilot group), 75, 150, or 300 IU (n=12 each) of XM17. The mean serum concentration-time profiles of XM17 revealed dose-related increases in maximum concentration (Cmax) within 24 hours followed by monoexponential decay for the three higher dose levels. Slopes estimated by linear regression for Cmax and AUC0-168h were ~1.0 (0.9052 IU/L and 1.0964 IU·h/L, respectively). For each IU of XM17 administered, Cmax and AUC0-168h rose by 0.032 IU/L and 2.60 IU·h/L, respectively. Geometric mean elimination half-life ranged from 54 to 90 hours. No antibodies to XM17 were detected. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events were headache (12 events in eleven [27.5%] subjects) and dizziness (four events in four [10%] subjects); two subjects (5%) reported mild pain on touch at the injection site.
Conclusion: Single subcutaneous doses of XM17 up to 300 IU in healthy young women exhibited dose-proportional pharmacokinetics with good safety and tolerability.
Keywords: anovulation; assisted reproductive technology; biosimilar; follitropin alfa.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase I, two-way, crossover study to demonstrate bioequivalence and to compare safety and tolerability of single-dose XM17 vs Gonal-f® in healthy women after follicle-stimulating hormone downregulation.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 1;13:130. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0124-y. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26621118 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, active-controlled, comparative phase 3 efficacy and safety equivalence trial of Ovaleap® (recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone) in infertile women using assisted reproduction technology (ART).Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016 Jan 6;14:1. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0135-8. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26733057 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A new fully human recombinant FSH (follitropin epsilon): two phase I randomized placebo and comparator-controlled pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic trials.Hum Reprod. 2017 Aug 1;32(8):1639-1647. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex220. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28591833 Clinical Trial.
-
XM17 Follitropin Alfa (Ovaleap(®)): A Review in Reproductive Endocrine Disorders.BioDrugs. 2016 Aug;30(4):379-86. doi: 10.1007/s40259-016-0183-4. BioDrugs. 2016. PMID: 27342604 Review.
-
Corifollitropin alfa: a review of its use in controlled ovarian stimulation for assisted reproduction.BioDrugs. 2011 Aug 1;25(4):243-54. doi: 10.2165/11206890-000000000-00000. BioDrugs. 2011. PMID: 21815699 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase I, two-way, crossover study to demonstrate bioequivalence and to compare safety and tolerability of single-dose XM17 vs Gonal-f® in healthy women after follicle-stimulating hormone downregulation.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 1;13:130. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0124-y. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26621118 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical trials for authorized biosimilars in the European Union: a systematic review.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;82(6):1444-1457. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13076. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27580073 Free PMC article.
-
Manufacturing of Recombinant Human Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Ovaleap® (XM17), Comparability with Gonal-f®, and Performance/Consistency.Drugs R D. 2017 Jun;17(2):305-312. doi: 10.1007/s40268-017-0182-z. Drugs R D. 2017. PMID: 28386738 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized, active-controlled, comparative phase 3 efficacy and safety equivalence trial of Ovaleap® (recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone) in infertile women using assisted reproduction technology (ART).Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016 Jan 6;14:1. doi: 10.1186/s12958-015-0135-8. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26733057 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of Ovaleap® (recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone) for up to 3 cycles in infertile women using assisted reproductive technology: a phase 3 open-label follow-up to Main Study.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016 Jun 10;14(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12958-016-0164-y. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27287439 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Dhillon S, Keating GM. Lutropin alfa. Drugs. 2008;68(11):1529–1540. - PubMed
-
- Durocher Y, Butler M. Expression systems for therapeutic glycoprotein production. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2009;20(6):700–707. - PubMed
-
- le Cotonnec JY, Porchet HC, Beltrami V, Khan A, Toon S, Rowland M. Clinical pharmacology of recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). I. Comparative pharmacokinetics with urinary human FSH. Fertil Steril. 1994;61(4):669–678. - PubMed
-
- Chambost H, Ljung R. Changing pattern of care of boys with haemophilia in western European centres. Haemophilia. 2005;11(2):92–99. - PubMed
-
- Daya S. Follicle-stimulating hormone in clinical practice: an update. Treat Endocrinol. 2004;3(3):161–171. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

