Space Weather Observations by GNSS Radio Occultation: From FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC to FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2
- PMID: 26213514
- PMCID: PMC4508922
- DOI: 10.1002/2014SW001133
Space Weather Observations by GNSS Radio Occultation: From FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC to FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2
Abstract
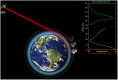
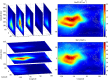
The joint Taiwan-United States FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC (Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate) mission, hereafter called COSMIC, is the first satellite constellation dedicated to remotely sense Earth's atmosphere and ionosphere using a technique called Global Positioning System (GPS) radio occultation (RO). The occultations yield abundant information about neutral atmospheric temperature and moisture as well as space weather estimates of slant total electron content, electron density profiles, and an amplitude scintillation index, S4. With the success of COSMIC, the United States and Taiwan are moving forward with a follow-on RO mission named FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 (COSMIC-2), which will ultimately place 12 satellites in orbit with two launches in 2016 and 2019. COSMIC-2 satellites will carry an advanced Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) RO receiver that will track both GPS and Russian Global Navigation Satellite System signals, with capability for eventually tracking other GNSS signals from the Chinese BeiDou and European Galileo system, as well as secondary space weather payloads to measure low-latitude plasma drifts and scintillation at multiple frequencies. COSMIC-2 will provide 4-6 times (10-15X in the low latitudes) the number of atmospheric and ionospheric observations that were tracked with COSMIC and will also improve the quality of the observations. In this article we focus on COSMIC/COSMIC-2 measurements of key ionospheric parameters.
Keywords: GNSS; ionosphere; radio occultation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Derivation of global ionospheric Sporadic E critical frequency (f o Es) data from the amplitude variations in GPS/GNSS radio occultations.R Soc Open Sci. 2020 Jul 22;7(7):200320. doi: 10.1098/rsos.200320. eCollection 2020 Jul. R Soc Open Sci. 2020. PMID: 32874629 Free PMC article.
-
The Marine Boundary Layer Height over the Western North Pacific Based on GPS Radio Occultation, Island Soundings, and Numerical Models.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Jan 4;19(1):155. doi: 10.3390/s19010155. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30621168 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Global Ionosphere TEC Maps with Satellite Altimetry and Ionospheric Radio Occultation Observations.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Dec 12;19(24):5489. doi: 10.3390/s19245489. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31842443 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Ionospheric Scintillation Models.Surv Geophys. 2015;36(2):295-324. doi: 10.1007/s10712-015-9319-1. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Surv Geophys. 2015. PMID: 26146426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of atmospheric gravity waves observed using the MU (Middle and Upper atmosphere) radar and GPS (Global Positioning System) radio occultation.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2014;90(1):12-27. doi: 10.2183/pjab.90.12. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24492645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Technical Design of a Low-Latitude Satellite Constellation for Ocean Observation with a Focus on Hainan Province, China.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;25(6):1710. doi: 10.3390/s25061710. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292774 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for meteotsunami detection in earth's atmosphere using GNSS observations.GPS Solut. 2023;27(4):169. doi: 10.1007/s10291-023-01492-8. Epub 2023 Jul 12. GPS Solut. 2023. PMID: 37457809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anthes RA, et al. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 Mission–Early results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008;89:313–333.
-
- Cook K, Wilczynski P. Wenkel M. 2014. The future of GNSS-RO for global weather monitoring and prediction—A COSMIC-2/FORMOSAT-7 Program status update, presented at the 8th FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC data users' workshop, Boulder, Colo.
-
- Coster A. Komjathy A. Space weather and the Global Positioning System. Space Weather. 2008;6 S06D04, doi: 10.1029/2008SW000400. - DOI
-
- da Silva Curiel A, Lambert M, Liddle D, Sweeting M, Chu V, Fong C-J. Chang G-S. 2013. Introduction to FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 mission, proceedings of the 27thAIAA/USU Conference on Small Satellites, Logan, Utah.
-
- Fong C-J, Chu V, Yen NL, Ling J, Liu J-Y. Chang G-S. 2012. FormoSat-7/COSMIC-2 Radio Occultation Mission: From research to operations, presented at the International Radio Occultation Working Group (IROWG) 2nd Workshop, Estes Park, Colo.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
